tidy3d.plugins.design.DesignSpace#
- class DesignSpace[source]#
Bases:
Tidy3dBaseModelManages all exploration of a parameter space within specified parameters using a supplied search method. The
DesignSpaceforms the basis of theDesignplugin, and receives aMethodandParameterlist that define the scope of the design space and how it should be searched.DesignSpace.run()can then be called with a function(s) to generate different solutions from parameters suggested by theMethod. TheMethodcan either sample the design space systematically or randomly, or can optimize for a given problem through an iterative search and evaluate approach.- Parameters:
attrs (dict = {}) – Dictionary storing arbitrary metadata for a Tidy3D object. This dictionary can be freely used by the user for storing data without affecting the operation of Tidy3D as it is not used internally. Note that, unlike regular Tidy3D fields,
attrsare mutable. For example, the following is allowed for setting anattrobj.attrs['foo'] = bar. Also note that Tidy3D will raise aTypeErrorifattrscontain objects that can not be serialized. One can check ifattrsare serializable by callingobj.json().parameters (Tuple[Union[ParameterInt, ParameterFloat, ParameterAny], ...] = ()) – Set of parameters defining the dimensions and allowed values for the design space.
method (Union[MethodMonteCarlo, MethodGrid, MethodBayOpt, MethodGenAlg, MethodParticleSwarm]) – Specifications for the procedure used to explore the parameter space.
task_name (str =) – Task name assigned to tasks along with a simulation counter in the form of {task_name}_{sim_index}_{counter} where
sim_indexis the index of theSimulationfrom the pre function output. If the pre function outputs a dictionary the key will be included in the task name as {task_name}_{dict_key}_{counter}. Only used when pre-post functions are supplied.name (Optional[str] = None) – Optional name for the design space.
path_dir (str = .) – Directory where simulation data files will be locally saved to. Only used when pre and post functions are supplied.
folder_name (str = default) – Folder path where the simulation will be uploaded in the Tidy3D Workspace. Will use ‘default’ if no path is set.
Notes
Schematic outline of how to use the
Designplugin to explore a design space.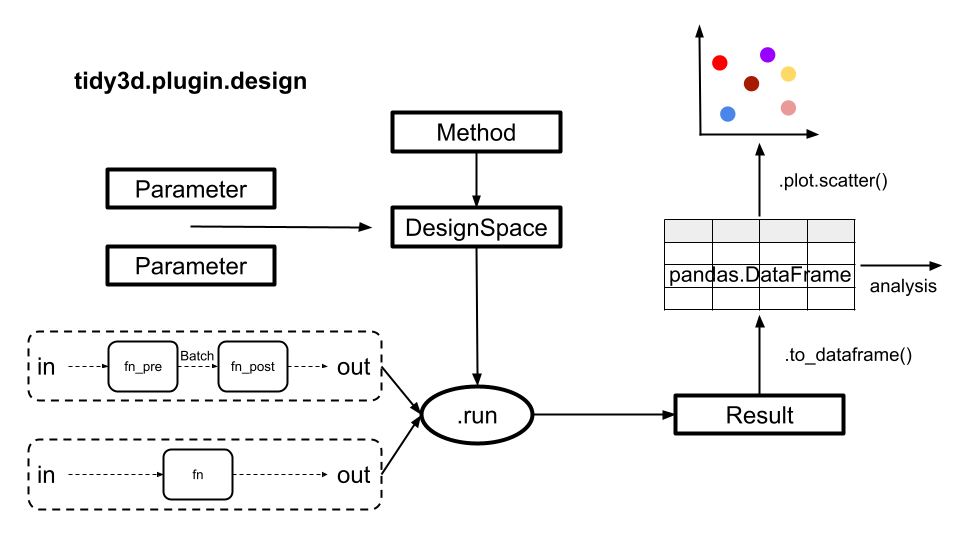
The Design notebook contains an overview of the
Designplugin and is the best place to learn how to get started. Detailed examples using theDesignplugin can be found in the following notebooks:Example
>>> import tidy3d.plugins.design as tdd >>> param = tdd.ParameterFloat(name="x", span=(0,1)) >>> method = tdd.MethodMonteCarlo(num_points=10) >>> design_space = tdd.DesignSpace(parameters=[param], method=method) >>> fn = lambda x: x**2 >>> result = design_space.run(fn) >>> df = result.to_dataframe() >>> im = df.plot()
Attributes
dimensions defined by the design parameter names.
methodDefines the methods used for parameter sweep.
Methods
estimate_cost(fn_pre)Compute the maximum FlexCredit charge for the
DesignSpace.runcomputation.get_fn_source(function)Get the function source as a string, return
Noneif not available.run(fn[, fn_post, verbose, priority])Explore a parameter space with a supplied method using the user supplied function.
run_batch(fn_pre, fn_post[, path_dir, priority])This function has been superceded by run, please use run for batched simulations.
run_pre_post(fn_pre, fn_post, console[, ...])Run a function with Tidy3D implicitly called in between.
run_single(fn, console)Run a single function of parameter inputs.
summarize([fn_pre, verbose])Summarize the setup of the DesignSpace
Inherited Common Usage
- parameters#
- method#
- task_name#
- name#
- path_dir#
- folder_name#
- property dims#
dimensions defined by the design parameter names.
- static get_fn_source(function)[source]#
Get the function source as a string, return
Noneif not available.
- run(fn, fn_post=None, verbose=True, priority=None)[source]#
Explore a parameter space with a supplied method using the user supplied function. Supplied functions are used to evaluate the design space and are called within the method. For optimization methods these functions act as the fitness function. A single function can be supplied which will contain the preprocessing, computation, and analysis of the desired problem. If running a Tidy3D simulation, it is recommended to split this function into a pre function, that creates a Simulation object(s), and a post function which analyses the SimulationData produced by the pre function Simulations. This allows the DesignSpace to manage the batching of Simulations, which varies between Method used, and saving time writing their own batching code. It also efficiently submits simulations to the cloud servers allowing for the fastest exploration of a design space.
The
fnfunction must take a dictionary input - this can be stored a dictionarydef example_fn(**params)or left as keyword argumentsdef example_fn(arg1, arg2)where the keywords correspond to thenameof the parameters in the design space.If used as a pre function, the output of
fnmust be a float,Simulation,Batch, list, or dict. SuppliedBatchobjects are run without modification and are run in series. A list or dict ofSimulationobjects is flattened into a singleBatchto enable parallel computation on the cloud. The original structure is then restored for output; allSimulationobjects are replaced bySimulationDataobjects. Example pre return formats and associated post inputs can be seen in the table below.Pre return formats and post input formats# fn_pre return
fn_post call
1.0
fn_post(1.0)
[1,2,3]
fn_post(1,2,3)
{‘a’: 2, ‘b’: ‘hi’}
fn_post(a=2, b=’hi’)
Simulation
fn_post(SimulationData)
Batch
fn_post(BatchData)
[Simulation, Simulation]
fn_post(SimulationData, SimulationData)
[Simulation, 1.0]
fn_post(SimulationData, 1.0)
[Simulation, Batch]
fn_post(SimulationData, BatchData)
{‘a’: Simulation, ‘b’: Batch, ‘c’: 2.0}
fn_post(a=SimulationData, b=BatchData, c=2.0)
The output of
fn_post(orfnif only one function is supplied) must be a float or a container where the first element is afloatand second element is alist/dicte,g. [float {“aux_1”: str}]. The float is used by the optimizers as the return of the fitness function. The second element is for auxiliary data from the analysis that the user may want to keep. Sampling methods (MethodGridorMethodMonteCarlo) can have any return type.- Parameters:
fn (Callable) – Function accepting arguments that correspond to the
namefields of theDesignSpace.parameters. Must return in the expected format for themethodused inDesignSpace, or return an object that fn_post can accept as an input.fn_post (Callable = None) – Optional function performing postprocessing on the output of
fn. It is recommended to supply fn_post when working with Simulation objects. Must return in the expected format for themethodused inDesignSpace.verbose (bool = True) – Toggle the output of statements stored in the logging console.
priority (int = None) – Optional vGPU queue priority (1 = lowest, 10 = highest) applied to simulations run via
fn/fn_post. Ignored whenfn_postis not provided because no automatic batching occurs in that mode.
- Returns:
Object containing the results of the design space exploration. Can be converted to
pandas.DataFramewith.to_dataframe().- Return type:
- run_pre_post(fn_pre, fn_post, console, priority=None)[source]#
Run a function with Tidy3D implicitly called in between.
- run_batch(fn_pre, fn_post, path_dir='.', priority=None, **batch_kwargs)[source]#
This function has been superceded by run, please use run for batched simulations.
- estimate_cost(fn_pre)[source]#
Compute the maximum FlexCredit charge for the
DesignSpace.runcomputation.Require a pre function that should return a
Simulationobject, aBatchobject, or collection of either. The pre function is called to estimate the cost - complicated pre functions may cause long runtimes. The cost per iteration is multiplied by the theoretical maximum number of iterations to give the maximum cost.- Parameters:
fn_pre (Callable) – Function accepting arguments that correspond to the
namefields of theDesignSpace.parameters. Should return aSimulationorBatchobject, or alist/dictof these objects.- Returns:
Estimated maximum cost for the
DesignSpace.run.- Return type:
float
- summarize(fn_pre=None, verbose=True)[source]#
Summarize the setup of the DesignSpace
Prints a summary of the DesignSpace including the method and associated args, the parameters, and the maximum number of runs expected. If
fn_preis provided an estimated cost will also be included. Additional notes are printed where relevant. All data is returned as a dict.- Parameters:
fn_pre (Callable = None) – Function accepting arguments that correspond to the
namefields of theDesignSpace.parameters. Allows for estimated cost to be included in the summary.verbose (bool = True) – Toggle if the summary should be output to log. If False, the dict is returned silently.
- Returns:
summary_dict – Dictionary containing the summary information.
- Return type:
dict
- __hash__()#
Hash method.