Technology and PDK Setup¶
This notebook builds a custom SiEPIC EBeam technology stack (PDK “technology”) intended for high-speed RF photonics work (modulators, transceivers), then validates/visualizes it by:
printing a technology summary (layers / extrusion specs / ports),
plotting a representative cross-section,
listing the available PDK components,
instantiating one example component.
Conventions
Geometry dimensions are in µm.
Frequencies are in Hz.
The PDK/technology in this project is implemented so that PIC designers can:
Understand the process stack quickly (layer thicknesses, materials, and key assumptions).
Modify the stack (e.g., oxide thickness, metal thickness/conductivity) without rewriting the whole PDK.
Translate the technology definition to other toolchains and formats.
In this notebook, the customization points are intentionally kept in a small set of named parameters (waveguide geometry, oxide stack, and metal stack), so you can reuse the same pattern for other foundry stacks.
Figure: The technology wrapper exposes a small set of parameters (materials + layer thicknesses) that define the process stack used in layout, visualization, and simulation.
Technology Stack Configuration¶
In the next cells we define the process stack parameters (waveguide geometry, oxide thicknesses, and metal stack) and the material models used by PhotonForge/Tidy3D.
The goal is to keep all tunable knobs centralized and clearly named so the stack can be reused across projects (or mapped to a foundry PDK).
This section sets up the SiEPIC EBeam technology with a few customizations aimed at high-speed RF photonics applications (modulators, transceivers).
Parameter |
Default PDK |
This Config |
|---|---|---|
top_oxide_thickness |
0.3 µm |
1.2 µm |
bottom_oxide_thickness |
3.017 µm |
2.0 µm |
metal_si_separation |
2.2 µm |
0.98 µm |
router_thickness |
0.6 µm |
2.0 µm |
router_metal |
Au (σ=17) |
Al (σ=38) |
include_top_opening |
False |
True |
include_substrate |
False |
True |
Key customizations vs ``siepic.ebeam()`` defaults
Thicker metal (2 µm Al) for better RF performance and lower loss.
Oxide thicknesses chosen to match a realistic process stack.
Higher conductivity Al for transmission-line electrodes.
Cross-section visualization includes air and substrate so the full stack is visible. This is aligned with the real chip stack where air and substrate are present.
[1]:
# Imports used throughout this notebook:
import tidy3d as td
import photonforge as pf
import numpy as np
import siepic_forge as siepic
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
[2]:
# Process / geometry parameters (units: µm)
# Waveguide geometry (kept consistent with the default EBeam PDK)
H_CORE = 0.22 # Silicon device/core thickness (µm)
H_SLAB = 0.09 # Silicon slab thickness for rib waveguides (µm)
W_CORE = 0.5 # Nominal waveguide width (µm)
# Oxide thicknesses
TOX_THICKNESS = 1.2 # Top oxide cladding thickness (µm)
BOX_THICKNESS = 2.0 # Buried oxide (BOX) thickness (µm)
# Metal stack (RF routing / heaters)
TL_THICKNESS = 2.0 # Router/heater metal thickness (µm)
METAL_SI_SEP = TOX_THICKNESS - H_CORE # Vertical gap between top Si and metal (µm)
[3]:
# Define aluminum for both optical and electrical simulations.
# We use Tidy3D's optical material model plus a (frequency-dependent) electrical medium.
al_metal = {
"optical": td.material_library["Al"]["Rakic1995"],
"electrical": td.LossyMetalMedium(
conductivity=38, # Conductivity in S/µm (≈ 38e6 S/m)
frequency_range=[0.1e9, 200e9], # Hz
fit_param=td.SurfaceImpedanceFitterParam(max_num_poles=16),
),
}
Create Custom Technology¶
Here we instantiate a Technology object by calling siepic.ebeam(...) and overriding the key stack parameters defined above.
The returned
techobject is used by PhotonForge for layout and for Tidy3D-based visualization/simulation.We also set
pf.config.default_technologyso subsequent components use this stack by default.
[4]:
# Build the Technology object with our custom stack parameters.
# This object controls layer definitions, vertical extrusions (cross-sections), and port definitions.
tech = siepic.ebeam(
# Si layer
si_thickness=H_CORE,
si_slab_thickness=H_SLAB,
# Oxide stack
top_oxide_thickness=TOX_THICKNESS,
bottom_oxide_thickness=BOX_THICKNESS,
# Metal stack
metal_si_separation=METAL_SI_SEP,
router_thickness=TL_THICKNESS,
router_metal=al_metal,
heater_metal=al_metal,
# Include surrounding media in the cross-section for visualization/simulation context
include_top_opening=True,
include_substrate=True,
)
# Revise the "TE_1550_500" port in accordance with W_CORE
tech.ports["TE_1550_500"].path_profiles = [(W_CORE, 0.0, (1, 0))]
# Set this technology as the default for the project
pf.config.default_technology = tech
[5]:
# Display a summary table of layers/ports/extrusions (sanity check)
tech
[5]:
Layers
| Name | Layer | Description | Color | Pattern |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | (1, 0) | Waveguides | #ff80a818 | \\ |
| PinRec | (1, 10) | SiEPIC | #00408018 | / |
| PinRecM | (1, 11) | SiEPIC | #00408018 | / |
| Si_Litho193nm | (1, 69) | Waveguides | #cc80a818 | \ |
| Waveguide | (1, 99) | Waveguides | #ff80a818 | \ |
| Si slab | (2, 0) | Waveguides | #80a8ff18 | / |
| SiN | (4, 0) | Waveguides | #a6cee318 | \\ |
| Oxide open (to BOX) | (6, 0) | Waveguides | #ffae0018 | \ |
| Text | (10, 0) | #0000ff18 | \ | |
| M1_heater | (11, 0) | Metal | #ebc63418 | xx |
| M2_router | (12, 0) | Metal | #90857018 | xx |
| M_Open | (13, 0) | Metal | #3471eb18 | xx |
| Si N | (20, 0) | Doping | #7000ff18 | \\ |
| Si N++ | (24, 0) | Doping | #0000ff18 | : |
| VC | (40, 0) | Metal | #3a027f18 | xx |
| DevRec | (68, 0) | SiEPIC | #00408018 | hollow |
| FbrTgt | (81, 0) | SiEPIC | #00408018 | / |
| FloorPlan | (99, 0) | Misc | #8000ff18 | hollow |
| SEM | (200, 0) | Misc | #ff00ff18 | \ |
| Deep Trench | (201, 0) | Misc | #c0c0c018 | solid |
| Keep out | (202, 0) | Misc | #a0a0c018 | // |
| Isolation Trench | (203, 0) | Misc | #c0c0c018 | solid |
| Dicing | (210, 0) | Misc | #a0a0c018 | solid |
| Chip design area | (290, 0) | Misc | #80005718 | hollow |
| FDTD | (733, 0) | SiEPIC | #80005718 | hollow |
| BlackBox | (998, 0) | SiEPIC | #00408018 | solid |
| Errors | (999, 0) | SiEPIC | #00008018 | / |
Extrusion Specs
| # | Mask | Limits (μm) | Sidewal (°) | Opt. Medium | Elec. Medium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | () | -inf, -2 | 0 | cSi_Li1993_293K | Si |
| 1 | () | 1.2, inf | 0 | Medium(permittivity=1.0) | Medium(permittivity=1.0) |
| 2 | 'Oxide open (to BOX)' | 0, inf | 0 | Medium(permittivity=1.0) | Medium(permittivity=1.0) |
| 3 | 'Si' | 0, 0.22 | 0 | cSi_Li1993_293K | Si |
| 4 | 'Si slab' | 0, 0.09 | 0 | cSi_Li1993_293K | Si |
| 5 | 'SiN' | 0, 0.4 | 0 | Si3N4_Luke2015_PMLStable | Si3N4 |
| 6 | 'M2_router' +…… 'M1_heater' | 1.2, 1.4 | 0 | Al_Rakic1995 | LossyMetalMedium……(frequency_range=(100000000.0, 200000000000.0), fit_param={'attrs': {}, 'max_num_poles': 16, 'tolerance_rms': 0.001, 'frequency_sampling_points': 20, 'log_sampling': True, 'type': 'SurfaceImpedanceFitterParam'}, conductivity=38.0) |
| 7 | 'M2_router' | 1.4, 3.2 | 0 | Al_Rakic1995 | LossyMetalMedium……(frequency_range=(100000000.0, 200000000000.0), fit_param={'attrs': {}, 'max_num_poles': 16, 'tolerance_rms': 0.001, 'frequency_sampling_points': 20, 'log_sampling': True, 'type': 'SurfaceImpedanceFitterParam'}, conductivity=38.0) |
| 8 | 'M_Open' | 3.2, inf | 0 | Medium(permittivity=1.0) | Medium(permittivity=1.0) |
| 9 | 'Deep Trench' +…… 'Isolation Trench' + 'Dicing' | -inf, inf | 0 | Medium(permittivity=1.0) | Medium(permittivity=1.0) |
Ports
| Name | Classification | Description | Width (μm) | Limits (μm) | Radius (μm) | Modes | Target n_eff | Path profiles (μm) | Voltage path | Current path |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MM_SiN_TE_1550_3000 | optical | Multimode SiN Strip TE 1550 nm,…… w=3000 nm | 8 | -2.5, 2.9 | 0 | 7 | 2.1 | 'SiN': 3 | ||
| MM_TE_1550_2000 | optical | Multimode Strip TE 1550 nm,…… w=2000 nm | 6 | -2, 2.22 | 0 | 12 | 3.5 | 'Si': 2 | ||
| MM_TE_1550_3000 | optical | Multimode Strip TE 1550 nm,…… w=3000 nm | 6 | -2, 2.22 | 0 | 17 | 3.5 | 'Si': 3 | ||
| Rib_TE_1310_350 | optical | Rib (90 nm slab) TE 1310 nm,…… w=350 nm | 2.35 | -1, 1.22 | 0 | 1 | 3.5 | 'Si': 0.35, 'Si…… slab': 3 | ||
| Rib_TE_1550_500 | optical | Rib (90 nm slab) TE 1550 nm,…… w=500 nm | 2.5 | -1, 1.22 | 0 | 1 | 3.5 | 'Si': 0.5, 'Si…… slab': 3 | ||
| SiN_TE-TM_1550_1000 | optical | SiN Strip TM 1550 nm, w=1000 nm | 3 | -1.5, 1.9 | 0 | 2 | 2.1 | 'SiN': 1 | ||
| SiN_TE_1310_750 | optical | SiN Strip TE 1310 nm, w=750 nm | 3 | -1, 1.4 | 0 | 1 | 2.1 | 'SiN': 0.75 | ||
| SiN_TE_1310_800 | optical | SiN Strip TE 1310 nm, w=800 nm | 3 | -1, 1.4 | 0 | 1 | 2.1 | 'SiN': 0.8 | ||
| SiN_TE_1550_1000 | optical | SiN Strip TE 1550 nm, w=1000 nm | 3 | -1, 1.4 | 0 | 1 | 2.1 | 'SiN': 1 | ||
| SiN_TE_1550_750 | optical | SiN Strip TE 1550 nm, w=750 nm | 3 | -1, 1.4 | 0 | 1 | 2.1 | 'SiN': 0.75 | ||
| SiN_TE_1550_800 | optical | SiN Strip TE 1550 nm, w=800 nm | 3 | -1, 1.4 | 0 | 1 | 2.1 | 'SiN': 0.8 | ||
| SiN_TE_895_450 | optical | SiN Strip TE 895 nm, w=450 nm | 2 | -1, 1.4 | 0 | 1 | 2.1 | 'SiN': 0.45 | ||
| SiN_TM_1310_750 | optical | SiN Strip TM 1310 nm, w=750 nm | 3 | -1.5, 1.9 | 0 | 1 + 1 (TM) | 2.1 | 'SiN': 0.75 | ||
| SiN_TM_1550_1000 | optical | SiN Strip TM 1550 nm, w=1000 nm | 3 | -1.5, 1.9 | 0 | 1 + 1 (TM) | 2.1 | 'SiN': 1 | ||
| Slot_TE_1550_500 | optical | Slot TE 1550 nm, w=500 nm,…… gap=100nm | 2 | -1, 1.22 | 0 | 1 | 3.5 | 'Si': 0.2 (-0.15),…… 'Si': 0.2 (+0.15) | ||
| TE-TM_1550_450 | optical | Strip TE-TM 1550, w=450 nm | 2 | -1, 1.22 | 0 | 2 | 3.5 | 'Si': 0.45 | ||
| TE_1310_350 | optical | Strip TE 1310 nm, w=350 nm | 2 | -1, 1.22 | 0 | 1 | 3.5 | 'Si': 0.35 | ||
| TE_1310_410 | optical | Strip TE 1310 nm, w=410 nm | 2 | -1, 1.22 | 0 | 1 | 3.5 | 'Si': 0.41 | ||
| TE_1550_500 | optical | Strip TE 1550 nm, w=500 nm | 2 | -1, 1.22 | 0 | 1 | 3.5 | 'Si': 0.5 | ||
| TM_1310_350 | optical | Strip TM 1310 nm, w=350 nm | 2 | -1, 1.22 | 0 | 1 + 1 (TM) | 3.5 | 'Si': 0.35 | ||
| TM_1550_500 | optical | Strip TM 1550 nm, w=500 nm | 2.5 | -1, 1.22 | 0 | 1 + 1 (TM) | 3.5 | 'Si': 0.5 | ||
| eskid_TE_1550 | optical | eskid TE 1550 | 3.31 | -1, 1.22 | 0 | 1 | 3.5 | 'Si': 0.35,…… 'Si': 0.06 (+0.265), 'Si': 0.06 (-0.265), 'Si': 0.06 (+0.385), 'Si': 0.06 (-0.385), 'Si': 0.06 (+0.505), 'Si': 0.06 (-0.505), 'Si': 0.06 (+0.625), 'Si': 0.06 (-0.625) |
Background medium
- Optical: SiO2_Palik_Lossless
- Electrical: SiO2
Plot technology cross-section¶
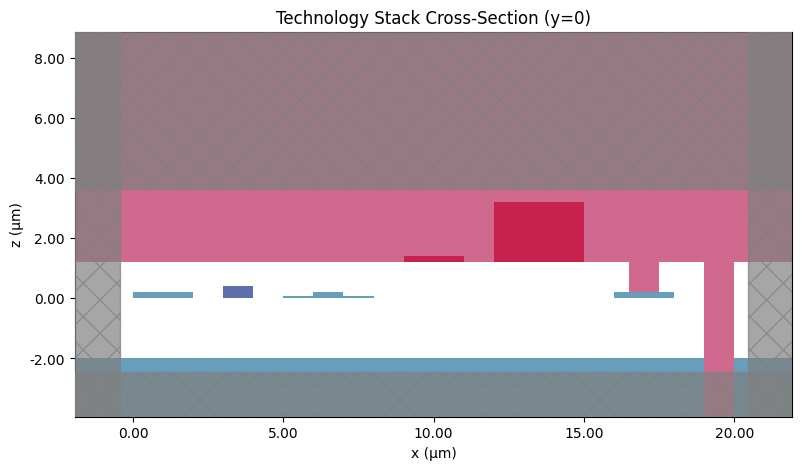
Before using the PDK in a larger design, it’s good practice to sanity-check the stack visually.
The helper function below:
builds a small “test” component containing shapes on representative layers (Si, SiN, metals, oxide opening, trench),
plots a cross-section at y = 0 using
pf.tidy3d_plot.
In the plot, x is the lateral position and z is the vertical stack height (both in µm).
[6]:
def plot_technology_cross_section(tech):
"""
Create a test component and plot its cross-section to visualize
the technology stack.
Args:
tech: PhotonForge Technology object
"""
# Create test component with various layer types
c = pf.Component("Technology_Cross_Section", technology=tech)
# Add test structures on different layers
c.add(
# Silicon waveguide (full etch)
"Si", pf.Rectangle((0, -0.5), (2, 0.5)),
# Silicon nitride
"SiN", pf.Rectangle((3, -0.5), (4, 0.5)),
# Rib waveguide (slab + core)
"Si slab", pf.Rectangle((5, -1.5), (8, 1.5)),
"Si", pf.Rectangle((6, -0.25), (7, 0.25)),
# Heater metal
"M1_heater", pf.Rectangle((9, -0.5), (11, 0.5)),
# Router metal with via opening
"M2_router", pf.Rectangle((12, -1), (15, 1)),
"M_Open", pf.Rectangle((13, -0.5), (14, 0.5)),
# Oxide opening (to BOX)
"Si", pf.Rectangle((16, -0.5), (18, 0.5)),
"Oxide open (to BOX)", pf.Rectangle((16.5, -0.3), (17.5, 0.3)),
# Deep trench
"Deep Trench", pf.Rectangle((19, -0.5), (20, 0.5)),
)
# Plot cross-section at y=0
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(14, 5))
pf.tidy3d_plot(c, y=0, ax=ax)
ax.set_title("Technology Stack Cross-Section (y=0)")
ax.set_xlabel("x (μm)")
ax.set_ylabel("z (μm)")
return c
[7]:
# Generate and display a simple cross-section sanity-check plot
plot_technology_cross_section(tech)
[7]:
List available components in the PDK¶
siepic_forge exposes the set of available components via siepic.component_names.
Use this list to discover valid names to instantiate with siepic.component(name).
[8]:
# All component names exposed by this PDK wrapper
siepic.component_names
[8]:
{'ANT_MMI_1x2_te1550_3dB_BB',
'GC_SiN_TE_1310_8degOxide_BB',
'GC_SiN_TE_1550_8degOxide_BB',
'GC_TE_1310_8degOxide_BB',
'GC_TE_1550_8degOxide_BB',
'GC_TM_1310_8degOxide_BB',
'GC_TM_1550_8degOxide_BB',
'crossing_horizontal',
'crossing_manhattan',
'ebeam_BondPad',
'ebeam_DC_2-1_te895',
'ebeam_DC_te895',
'ebeam_MMI_2x2_5050_te1310',
'ebeam_Polarizer_TM_1550_UQAM',
'ebeam_YBranch_895',
'ebeam_YBranch_te1310',
'ebeam_adiabatic_te1550',
'ebeam_adiabatic_tm1550',
'ebeam_bdc_te1550',
'ebeam_crossing4',
'ebeam_gc_te1550',
'ebeam_gc_te895',
'ebeam_gc_tm1550',
'ebeam_routing_taper_te1550_w=500nm_to_w=3000nm_L=20um',
'ebeam_routing_taper_te1550_w=500nm_to_w=3000nm_L=40um',
'ebeam_splitter_swg_assist_te1310',
'ebeam_splitter_swg_assist_te1550',
'ebeam_terminator_SiN_1550',
'ebeam_terminator_SiN_te895',
'ebeam_terminator_te1310',
'ebeam_terminator_te1550',
'ebeam_terminator_tm1550',
'ebeam_y_1550',
'ebeam_y_adiabatic',
'ebeam_y_adiabatic_500pin',
'taper_SiN_750_3000',
'taper_si_simm_1310',
'taper_si_simm_1550'}
Load an example PDK component¶
Below we instantiate one component from the library and render it.
This is a quick check that the PDK is installed correctly and that the component’s layers/ports are available.
Tip: replace the component name with any entry from siepic.component_names.
[9]:
# Instantiate one component by name (change this string to explore the library)
siepic.component("ebeam_y_adiabatic_500pin")
[9]: