tidy3d.ModeSource#
- class ModeSource[source]#
Bases:
DirectionalSource,PlanarSource,BroadbandSourceInjects current source to excite modal profile on finite extent plane.
- Parameters:
name (Attribute:
name) –TypeOptional[str]
Default= None
DescriptionOptional name for the source.
center (Attribute:
center) –TypeTuple[float, float, float]
Default= (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
Unitsum
DescriptionCenter of object in x, y, and z.
size (Attribute:
size) –TypeTuple[NonNegativeFloat, NonNegativeFloat, NonNegativeFloat]
DefaultUnitsum
DescriptionSize in x, y, and z directions.
source_time (Attribute:
source_time) –TypeUnion[GaussianPulse, ContinuousWave, CustomSourceTime]
DefaultDescriptionSpecification of the source time-dependence.
num_freqs (Attribute:
num_freqs) –TypeConstrainedIntValue
Default= 1
DescriptionNumber of points used to approximate the frequency dependence of injected field. A Chebyshev interpolation is used, thus, only a small number of points, i.e., less than 20, is typically sufficient to obtain converged results.
direction (Attribute:
direction) –TypeLiteral[‘+’, ‘-‘]
DefaultDescriptionSpecifies propagation in the positive or negative direction of the injection axis.
mode_spec (Attribute:
mode_spec) –TypeModeSpec
Default= ModeSpec(num_modes1, target_neffNone, num_pml(0,, 0), filter_polNone, angle_theta0.0, angle_phi0.0, precision’single’, bend_radiusNone, bend_axisNone, track_freq’central’, group_index_stepFalse, type’ModeSpec’)
DescriptionParameters to feed to mode solver which determine modes measured by monitor.
mode_index (Attribute:
mode_index) –TypeNonNegativeInt
Default= 0
DescriptionIndex into the collection of modes returned by mode solver. Specifies which mode to inject using this source. If larger than
mode_spec.num_modes,num_modesin the solver will be set tomode_index + 1.
Notes
Using this mode source, it is possible selectively excite one of the guided modes of a waveguide. This can be computed in our eigenmode solver
tidy3d.plugins.mode.ModeSolverand implement the mode simulation in FDTD.Mode sources are normalized to inject exactly 1W of power at the central frequency.
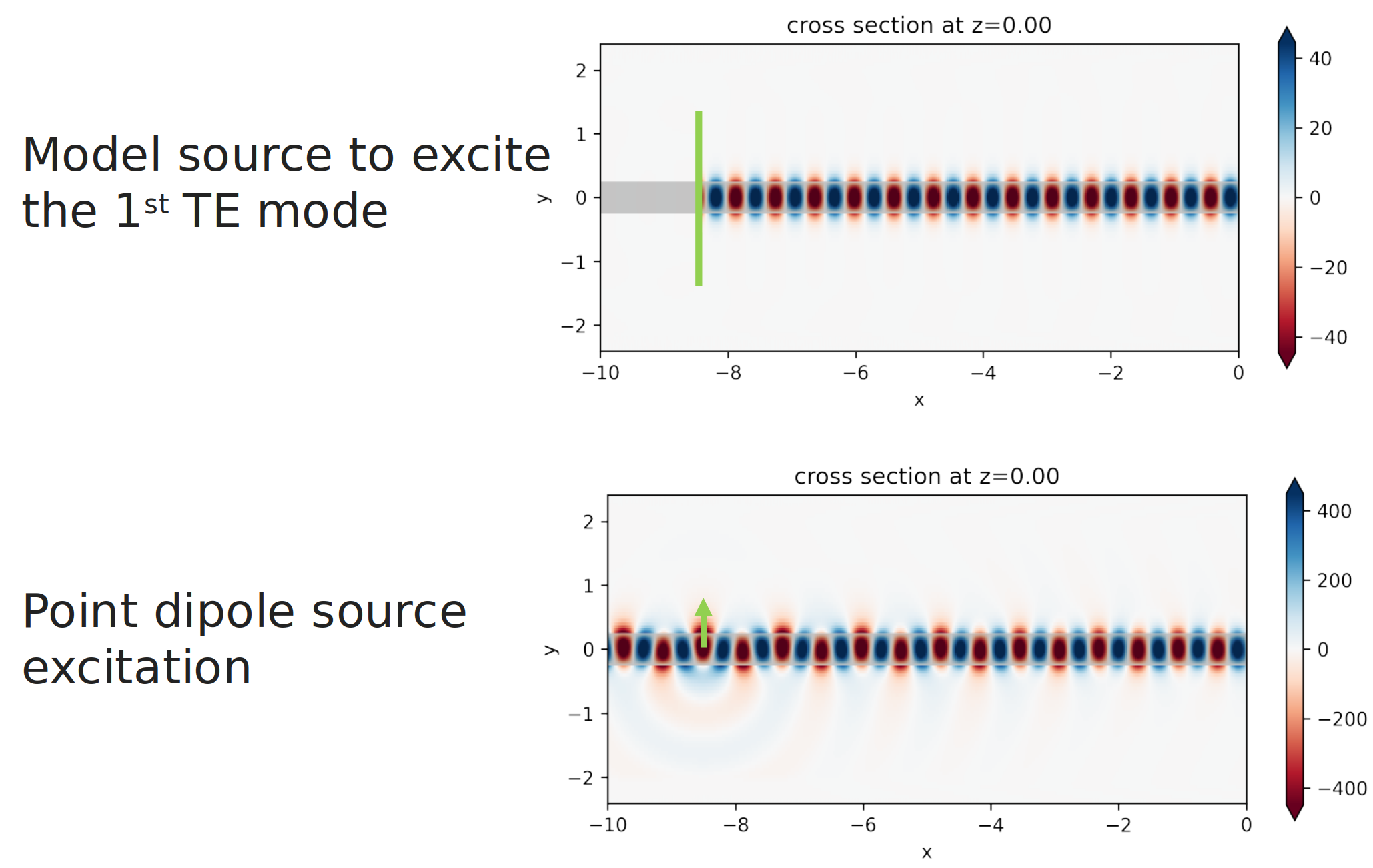
The modal source allows you to do directional excitation. Illustrated by the image below, the field is perfectly launched to the right of the source and there’s zero field to the left of the source. Now you can contrast the behavior of the modal source with that of a dipole source. If you just put a dipole into the waveguide, well, you see quite a bit different in the field distribution. First of all, the dipole source is not directional launching. It launches waves in both directions. The second is that the polarization of the dipole is set to selectively excite a TE mode. But it takes some propagation distance before the mode settles into a perfect TE mode profile. During this process, there is radiation into the substrate.
Example
>>> pulse = GaussianPulse(freq0=200e12, fwidth=20e12) >>> mode_spec = ModeSpec(target_neff=2.) >>> mode_source = ModeSource( ... size=(10,10,0), ... source_time=pulse, ... mode_spec=mode_spec, ... mode_index=1, ... direction='-')
See also
tidy3d.plugins.mode.ModeSolver:Interface for solving electromagnetic eigenmodes in a 2D plane with translational invariance in the third dimension.
- Notebooks:
- Lectures:
Attributes
Azimuth angle of propagation.
Polar angle of propagation.
Methods
- mode_spec#
- mode_index#
- property angle_theta#
Polar angle of propagation.
- property angle_phi#
Azimuth angle of propagation.
- __hash__()#
Hash method.