Tidy3D Documentation
Contents
Tidy3D Documentation#
Tidy3D is a software package for solving extremely large electrodynamics problems using the finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) method. It can be controlled through either an open source python package or a web-based graphical user interface.
If you’d rather skip installation and run an example in one of our web-hosted notebooks, click here.
1. Set up Tidy3D#
Install the python library tidy3d for creating, managing, and postprocessing simulations with
pip install tidy3d
Next, configure your tidy3d package with the API key from your account.
tidy3d configure
And enter your API key when prompted.
For more detailed installation instructions, see this page.
2. Run a Simulation#
Start running simulations with just a few lines of code. Run this sample code to simulate a 3D dielectric box in Tidy3D and plot the corresponding field pattern.
# !pip install tidy3d # if needed, install tidy3d in a notebook by uncommenting this line
# import the tidy3d package and configure it with your API key
import numpy as np
import tidy3d as td
import tidy3d.web as web
# web.configure("YOUR API KEY") # if authentication needed, uncomment this line and paste your API key here
# set up global parameters of simulation ( speed of light / wavelength in micron )
freq0 = td.C_0 / 0.75
# create structure - a box centered at 0, 0, 0 with a size of 1.5 micron and permittivity of 2
square = td.Structure(
geometry=td.Box(center=(0, 0, 0), size=(1.5, 1.5, 1.5)),
medium=td.Medium(permittivity=2.0)
)
# create source - A point dipole source with frequency freq0 on the left side of the domain
source = td.PointDipole(
center=(-1.5, 0, 0),
source_time=td.GaussianPulse(freq0=freq0, fwidth=freq0 / 10.0),
polarization="Ey",
)
# create monitor - Measures electromagnetic fields within the entire domain at z=0
monitor = td.FieldMonitor(
size=(td.inf, td.inf, 0),
freqs=[freq0],
name="fields",
colocate=True,
)
# Initialize simulation - Combine all objects together into a single specification to run
sim = td.Simulation(
size=(4, 3, 3),
grid_spec=td.GridSpec.auto(min_steps_per_wvl=25),
structures=[square],
sources=[source],
monitors=[monitor],
run_time=120/freq0,
)
print(f"simulation grid is shaped {sim.grid.num_cells} for {int(np.prod(sim.grid.num_cells)/1e6)} million cells.")
# run simulation through the cloud and plot the field data computed by the solver and stored in the monitor
data = td.web.run(sim, task_name="quickstart", path="data/data.hdf5", verbose=True)
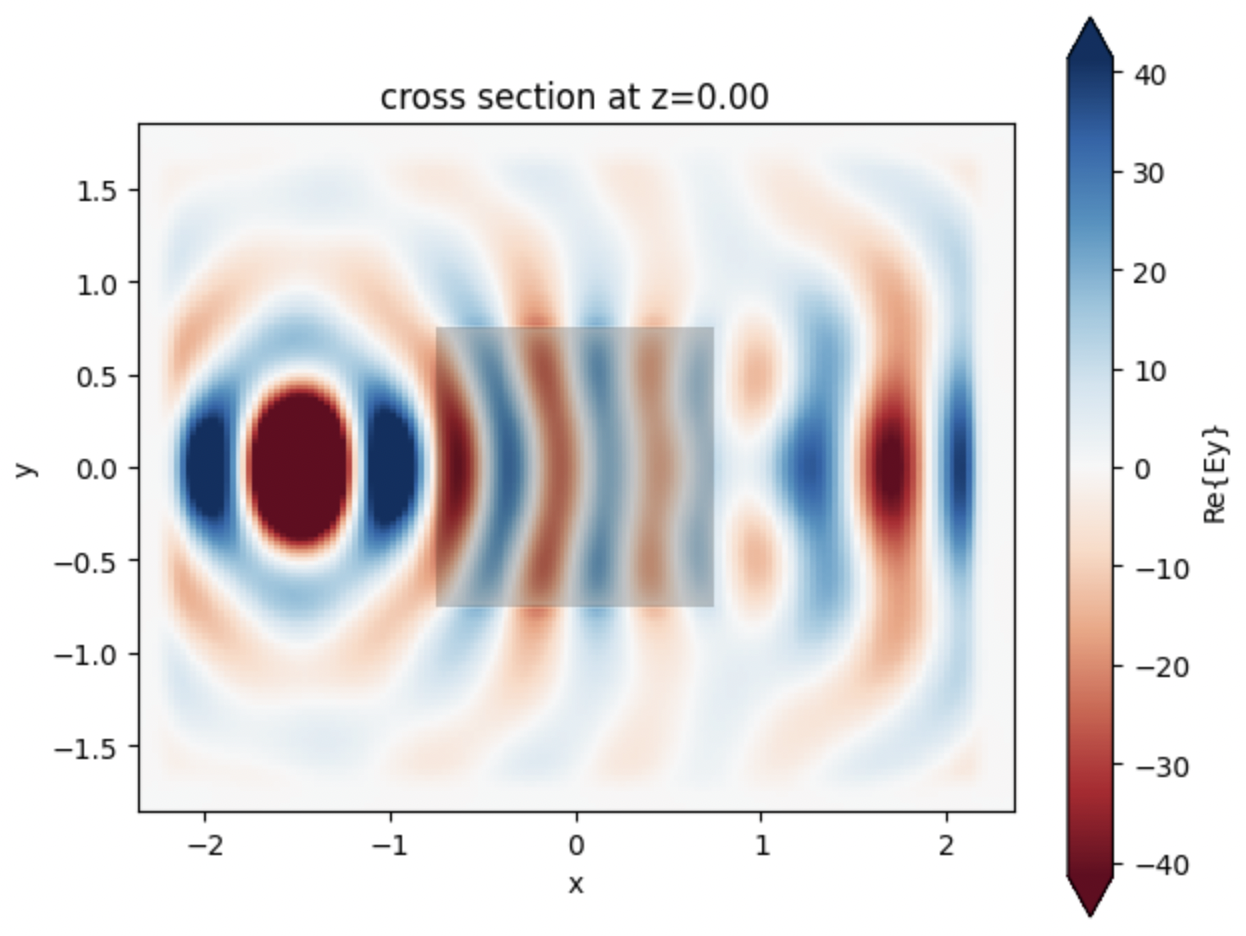
ax = data.plot_field("fields", "Ey", z=0)
This will produce the following plot, which visualizes the electromagnetic fields on the central plane.
3. Analyze Results#
Postprocess simulation data using the same python session, or
View the results of this simulation on our web-based graphical user interface.