tidy3d.LinearLumpedElement#
- class LinearLumpedElement[source]#
Bases:
RectangularLumpedElementLumped element representing a network consisting of resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
- Parameters:
attrs (dict = {}) – Dictionary storing arbitrary metadata for a Tidy3D object. This dictionary can be freely used by the user for storing data without affecting the operation of Tidy3D as it is not used internally. Note that, unlike regular Tidy3D fields,
attrsare mutable. For example, the following is allowed for setting anattrobj.attrs['foo'] = bar. Also note that Tidy3D` will raise aTypeErrorifattrscontain objects that can not be serialized. One can check ifattrsare serializable by callingobj.json().center (Union[tuple[Union[float, autograd.tracer.Box], Union[float, autograd.tracer.Box], Union[float, autograd.tracer.Box]], Box] = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)) – [units = um]. Center of object in x, y, and z.
size (Union[tuple[Union[pydantic.v1.types.NonNegativeFloat, autograd.tracer.Box], Union[pydantic.v1.types.NonNegativeFloat, autograd.tracer.Box], Union[pydantic.v1.types.NonNegativeFloat, autograd.tracer.Box]], Box]) – [units = um]. Size in x, y, and z directions.
name (ConstrainedStrValue) – Unique name for the lumped element.
num_grid_cells (Optional[PositiveInt] = 3) – Number of mesh grid cells associated with the lumped element along each direction. Used in generating the suggested list of
MeshOverrideStructureobjects. A value ofNonewill turn off mesh refinement suggestions.voltage_axis (Literal[0, 1, 2]) – Specifies the axis along which the component is oriented and along which the associated voltage drop will occur. Must be in the plane of the element.
snap_perimeter_to_grid (bool = True) – When enabled, the perimeter of the lumped element is snapped to the simulation grid, which improves accuracy when the number of grid cells is low within the element. Sides of the element perpendicular to the
voltage_axisare snapped to grid boundaries, while the sides parallel to thevoltage_axisare snapped to grid centers. Lumped elements are always snapped to the nearest grid boundary along theirnormal_axis, regardless of this option.network (Union[RLCNetwork, AdmittanceNetwork]) – The linear element produces an equivalent medium that emulates the voltage-current relationship described by the
networkfield.dist_type (Literal['off', 'laterally_only', 'on'] = on) – Switches between the different methods for distributing the lumped element over the grid.
Notes
Implementation is based on the equivalent medium introduced by [1].
References
Example
>>> RL_series = RLCNetwork(resistance=75, ... inductance=1e-9, ... network_topology="series" ... ) >>> linear_element = LinearLumpedElement( ... center=[0, 0, 0], ... size=[2, 0, 3], ... voltage_axis=0, ... network=RL_series, ... name="LumpedRL" ... )
See also
- Notebooks:
Attributes
Methods
admittance(freqs)Returns the admittance of this lumped element at the frequencies specified by
freqs.Provides an estimate for the parasitic inductance and capacitance associated with the connections.
impedance(freqs)Returns the impedance of this lumped element at the frequencies specified by
freqs.to_PEC_connection(grid)Converts the
LinearLumpedElementobject to aStructure, representing any PEC connections.to_structure(grid)Converts the
LinearLumpedElementobject to aStructure, which enforces the desired voltage-current relationship across one or more grid cells.to_structures(grid)Converts the
LinearLumpedElementobject to a list ofStructurewhich are ready to be added to theSimulationInherited Common Usage
- network#
- dist_type#
An advanced feature for
LinearLumpedElementis the ability to choose different methods for distributing the network portion over the the Yee grid. When set toon, the network portion of the lumped element is distributed across the entirety of the lumped element’s bounding box. When set tooff, the network portion of the lumped element is restricted to one cell and PEC connections are used to connect the network cell to the edges of the lumped element. A third option existslaterally_only, where the network portion is only distributed along the lateral axis of the lumped element.When using a
dist_typeother thanonadditional parasitic network elements are introduced, see below. Thin connections lead to a higher inductance, while wide connections lead to a higher parasitic capacitance. Follow the link to the associated notebook for an example of using this field.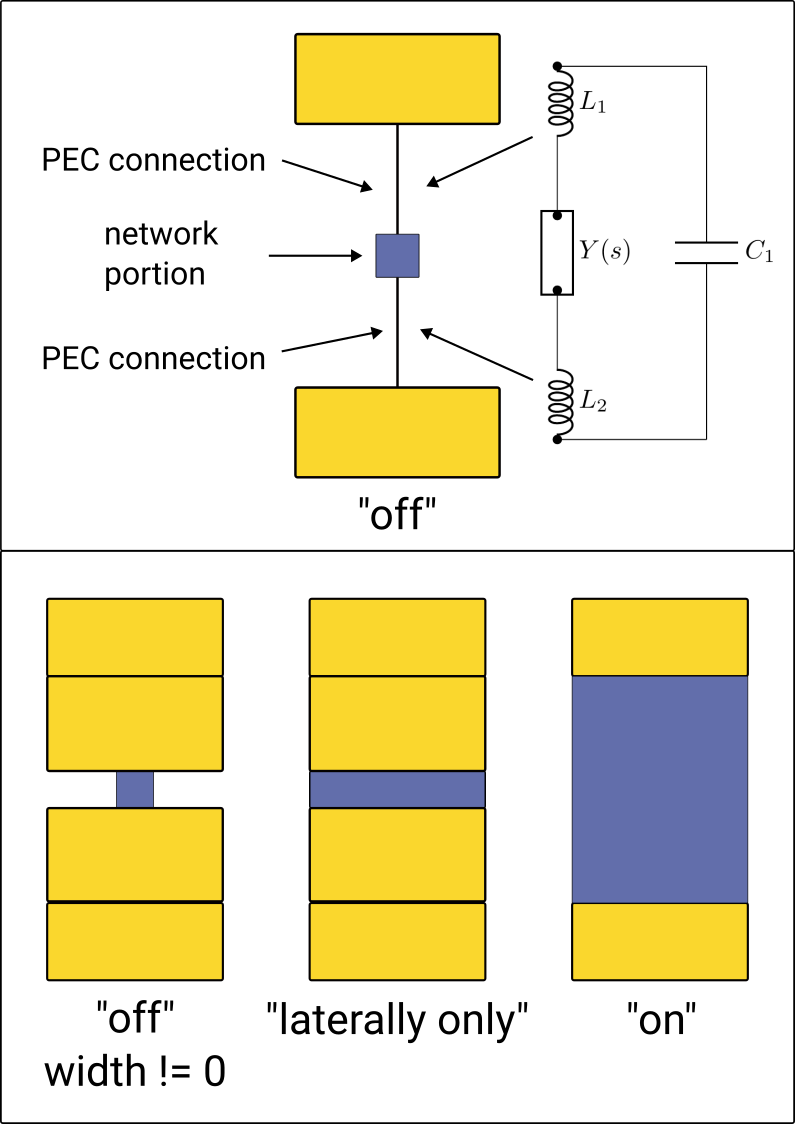
See also
- Notebooks:
- to_structure(grid)[source]#
Converts the
LinearLumpedElementobject to aStructure, which enforces the desired voltage-current relationship across one or more grid cells.
- to_PEC_connection(grid)[source]#
Converts the
LinearLumpedElementobject to aStructure, representing any PEC connections.
- to_structures(grid)[source]#
Converts the
LinearLumpedElementobject to a list ofStructurewhich are ready to be added to theSimulation
- estimate_parasitic_elements(grid)[source]#
Provides an estimate for the parasitic inductance and capacitance associated with the connections. These wire or sheet connections are used when the lumped element is not distributed over the voltage axis.
Notes
These estimates for parasitic inductance and capacitance are approximate and may be inaccurate in some cases. However, the formulas used should be accurate in the important regime where the true values for inductance and capacitance are large. For example, the estimate for capacitance will be more accurate for wide elements discretized with a high resolution grid.
- Returns:
A tuple containing the parasitic series inductance and parasitic shunt capacitance, respectively.
- Return type:
tuple[float, float]
- admittance(freqs)[source]#
Returns the admittance of this lumped element at the frequencies specified by
freqs.Note
Admittance is returned using the physics convention for time-harmonic fields \(\exp{-j \omega t}\), so the imaginary part of the admittance will have an opposite sign compared to the expected value when using the engineering convention.
- impedance(freqs)[source]#
Returns the impedance of this lumped element at the frequencies specified by
freqs.Note
Impedance is returned using the physics convention for time-harmonic fields \(\exp{-j \omega t}\), so the imaginary part of the impedance will have an opposite sign compared to the expected value when using the engineering convention.
- __hash__()#
Hash method.