Edge-mounted SMA to co-planar waveguide transition#
The subminiature version A (SMA) coaxial connector is an essential component in printed circuit board (PCB) applications. It is commonly used as the interface between the on-board circuit and external components such as antennas or measurement devices.
In this notebook, we model two edge-mounted SMA connectors attached to a grounded co-planar waveguide (CPW). The connector-to-connector insertion and return losses are calculated to ensure proper impedance matching and minimal reflection.
[1]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tidy3d as td
import tidy3d.plugins.microwave as mw
import tidy3d.plugins.smatrix as sm
from tidy3d import web
td.config.logging_level = "ERROR"
Building the Simulation#
Key Parameters#
[2]:
# Frequencies and bandwidth
(f_min, f_max) = (1e9, 10e9)
f0 = (f_min + f_max) / 2
freqs = np.linspace(f_min, f_max, 301)
Important geometry dimensions are defined below. The default length unit is microns, so we introduce a mm conversion factor.
[3]:
mm = 1000 # Conversion factor mm to microns
# Coaxial dimensions (50 ohm)
R0 = 0.635 * mm # Coax inner radius
R1 = 2.125 * mm # Coax outer radius
# Substrate overall dimensions
H = 1.57 * mm # Substrate thickness
Lsub, Wsub = (83 * mm, 30 * mm) # PCB board dimensions
# Transmission line dimensions
T = 0.038 * mm # Metal thickness
WS = 2.58 * mm # Signal trace width
G = 1 * mm # CPW gap width
WG = 5 * mm # Side ground trace width
# Via dimensions
VR = 0.5 * mm # Via radius
VP = 3 * mm # Via pitch, longitudinal
VL = 3 * mm # Via pitch, transverse
VS = 1 * mm # Via start z-coordinate
# Edge mount dimensions
Voffset = 0.125 * mm # SMA connector vertical offset
Medium and Structures#
Below, we define the materials used in model:
PTFE for the SMA dielectric core
Gold for the SMA body
FR4 for the PCB substrate
Copper for the PCB traces
[4]:
med_FR4 = td.Medium(permittivity=4.4)
med_PTFE = td.Medium(permittivity=2.1)
med_Cu = td.LossyMetalMedium(conductivity=60, frequency_range=(f_min, f_max)) # [S/um]
med_Au = td.LossyMetalMedium(conductivity=41, frequency_range=(f_min, f_max)) # [S/um]
The SMA geometry is imported from a STL file, and then translated and rotated to the appropriate position. The SMA core is created from a td.Cylinder instance. To ensure a close fit, we initialize the SMA core to be slightly larger than the inner radius and use Boolean subtraction to cut it to size.
[5]:
# Import SMA geometry
geom_SMA = td.TriangleMesh.from_stl(filename="./misc/SMA_model.stl", scale=mm, origin=(0, 0, 0))
geom_SMA = (geom_SMA.rotated(np.pi / 2, 0)).rotated(np.pi, 2)
geom_SMA = geom_SMA.translated(0, Voffset, 0)
# Create SMA dielectric core
geom_SMA_diel = td.Cylinder(
center=(0, Voffset, -6 * mm / 2), radius=1.1 * R1, length=6 * mm, axis=2
)
geom_SMA_diel -= geom_SMA
We also make a copy for a second connector.
[6]:
# Make copy for second connector
geom_SMA2 = (geom_SMA.rotated(np.pi, 1)).translated(0, 0, Lsub)
geom_SMA_diel2 = (geom_SMA_diel.rotated(np.pi, 1)).translated(0, 0, Lsub)
The substrate and CPW geometries are created below.
[7]:
# Substrate
geom_sub = td.Box.from_bounds(rmin=(-Wsub / 2, -H - T, 0), rmax=(Wsub / 2, -T, Lsub))
# Transmission line and connecting structures
geom_sig = td.Box.from_bounds(rmin=(-WS / 2, -T, 0), rmax=(WS / 2, 0, Lsub))
geom_gnd1 = td.Box.from_bounds(rmin=(-WS / 2 - G - WG, -T, 0), rmax=(-WS / 2 - G, 0, Lsub))
geom_gnd2 = geom_gnd1.reflected((1, 0, 0))
geom_line = td.GeometryGroup(geometries=[geom_sig, geom_gnd1, geom_gnd2])
geom_gnd = td.Box.from_bounds(rmin=(-Wsub / 2, -H - 2 * T, 0), rmax=(Wsub / 2, -H - T, Lsub))
To ensure proper transmission in the high frequency range, we create a via fence that encloses the signal trace.
[8]:
# Create via fence
def create_via_hole(xpos, zpos):
geom = td.Cylinder(center=(xpos, -H / 2 - T, zpos), axis=1, length=H, radius=VR)
return geom
geom_via_array = []
zpos = VS
while zpos < Lsub - VS + 0.1 * mm:
for xpos in [-VL, VL]:
geom_via_array += [create_via_hole(xpos, zpos)]
zpos += VP
geom_via_group = td.GeometryGroup(geometries=geom_via_array)
We combine the previously defined geometries and materials into Structure instances, ready for simulation.
[9]:
# Create structures
str_SMA = td.Structure(geometry=geom_SMA, medium=med_Au)
str_SMA2 = td.Structure(geometry=geom_SMA2, medium=med_Au)
str_SMA_diel = td.Structure(geometry=geom_SMA_diel, medium=med_PTFE)
str_SMA_diel2 = td.Structure(geometry=geom_SMA_diel2, medium=med_PTFE)
str_sub = td.Structure(geometry=geom_sub, medium=med_FR4)
str_line = td.Structure(geometry=geom_line, medium=med_Cu)
str_gnd = td.Structure(geometry=geom_gnd, medium=med_Cu)
str_vias = td.Structure(geometry=geom_via_group, medium=med_Cu)
# List of all structures
structure_list = [
str_SMA,
str_SMA2,
str_SMA_diel,
str_SMA_diel2,
str_sub,
str_line,
str_gnd,
str_vias,
]
Grid and Boundaries#
The simulation boundaries are open (PML) on all sides. We introduce a padding of wavelength/2 on all sides to ensure that the external boundaries do not encroach on the near-field.
[10]:
# Define simulation size and center
padding = td.C_0 / f0 / 2
sim_LZ = Lsub + padding
sim_LX = Wsub + padding
sim_LY = 5 * mm + padding
sim_center = (0, 0, Lsub / 2)
The grid refinement strategy is as follows:
Use
LayerRefinementSpecfor PCB metallic layersUse
MeshOverrideStructurefor SMA dielectric core and metal via fences
[11]:
# Define layer refinement spec
lr_options = {
"corner_refinement": td.GridRefinement(dl=0.1 * mm, num_cells=2),
"min_steps_along_axis": 1,
}
lr1 = td.LayerRefinementSpec.from_structures(structures=[str_line], **lr_options)
lr2 = td.LayerRefinementSpec.from_structures(structures=[str_gnd], **lr_options)
# Define mesh override around SMA core and vias
rbox1 = td.MeshOverrideStructure(
geometry=geom_SMA_diel.bounding_box, dl=(0.2 * mm, 0.2 * mm, 0.2 * mm)
)
rbox2 = td.MeshOverrideStructure(
geometry=geom_SMA_diel2.bounding_box, dl=(0.2 * mm, 0.2 * mm, 0.2 * mm)
)
rbox_vias = []
for geom in geom_via_array:
rbox_vias += [
td.MeshOverrideStructure(geometry=geom.bounding_box, dl=(0.3 * mm, None, 0.3 * mm))
]
The overall grid specification is defined below.
[12]:
# Define overall grid specification
grid_spec = td.GridSpec.auto(
min_steps_per_wvl=12,
wavelength=td.C_0 / f_max,
layer_refinement_specs=[lr1, lr2],
override_structures=[rbox1, rbox2] + rbox_vias,
)
Monitors#
We define some field monitors for visualization purposes below.
[13]:
# Field Monitor
mon_1 = td.FieldMonitor(
center=(0, -T - H / 2, 0),
size=(td.inf, 0, td.inf),
freqs=[f_min, f0, f_max],
name="field in-plane",
)
mon_2 = td.FieldMonitor(
center=(0, 0, 0),
size=(0, td.inf, td.inf),
freqs=[f_min, f0, f_max],
name="field cross section",
)
# List of all monitors
monitor_list = [mon_1, mon_2]
Ports#
Wave ports are positioned along the coaxial section of each SMA connector.
[14]:
# Wave port position and dimension
wp_offset = 4 * mm # longitudinal offset
w_port = 8 * mm # port width and height
# Current integral for port impedance calculation
I_int = mw.CurrentIntegralAxisAligned(
center=(0, Voffset, -wp_offset), size=(R0 + R1, R0 + R1, 0), sign="+"
)
# Define wave ports
WP1 = sm.WavePort(
center=(0, Voffset, -wp_offset),
size=(w_port, w_port, 0),
mode_spec=td.ModeSpec(target_neff=np.sqrt(2.1)),
direction="+",
name="WP1",
current_integral=I_int,
frame=None,
)
WP2 = WP1.updated_copy(
center=(0, Voffset, Lsub + wp_offset),
direction="-",
name="WP2",
current_integral=I_int.updated_copy(center=(0, Voffset, Lsub + wp_offset), sign="-"),
)
Defining Simulation and TerminalComponentModeler#
The Simulation and TerminalComponentModeler instances are defined below.
[15]:
sim = td.Simulation(
center=sim_center,
size=(sim_LX, sim_LY, sim_LZ),
grid_spec=grid_spec,
structures=structure_list,
monitors=monitor_list,
run_time=5e-9,
plot_length_units="mm",
symmetry=(1, 0, 0),
)
tcm = sm.TerminalComponentModeler(
simulation=sim,
ports=[WP1, WP2],
freqs=freqs,
)
Visualization#
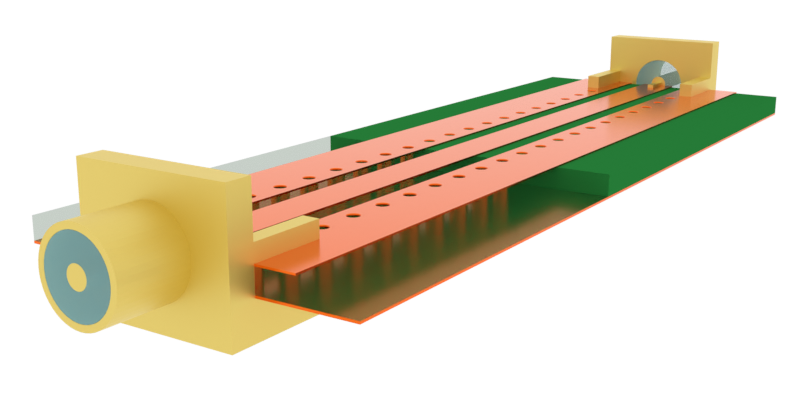
Before running, it is a good idea to check the structure layout and simulation grid. Below, the top and side cross-sections of the structure is shown, along with the wave ports sources (green arrow) and internal modal absorbers (blue arrow).
[16]:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 10), tight_layout=True)
tcm.plot_sim(
y=-T, ax=ax[0], monitor_alpha=0, hlim=(-20 * mm, 20 * mm), vlim=(-15 * mm, Lsub + 15 * mm)
)
tcm.plot_sim(
x=0, ax=ax[1], monitor_alpha=0, hlim=(-10 * mm, 10 * mm), vlim=(-15 * mm, Lsub + 15 * mm)
)
plt.show()
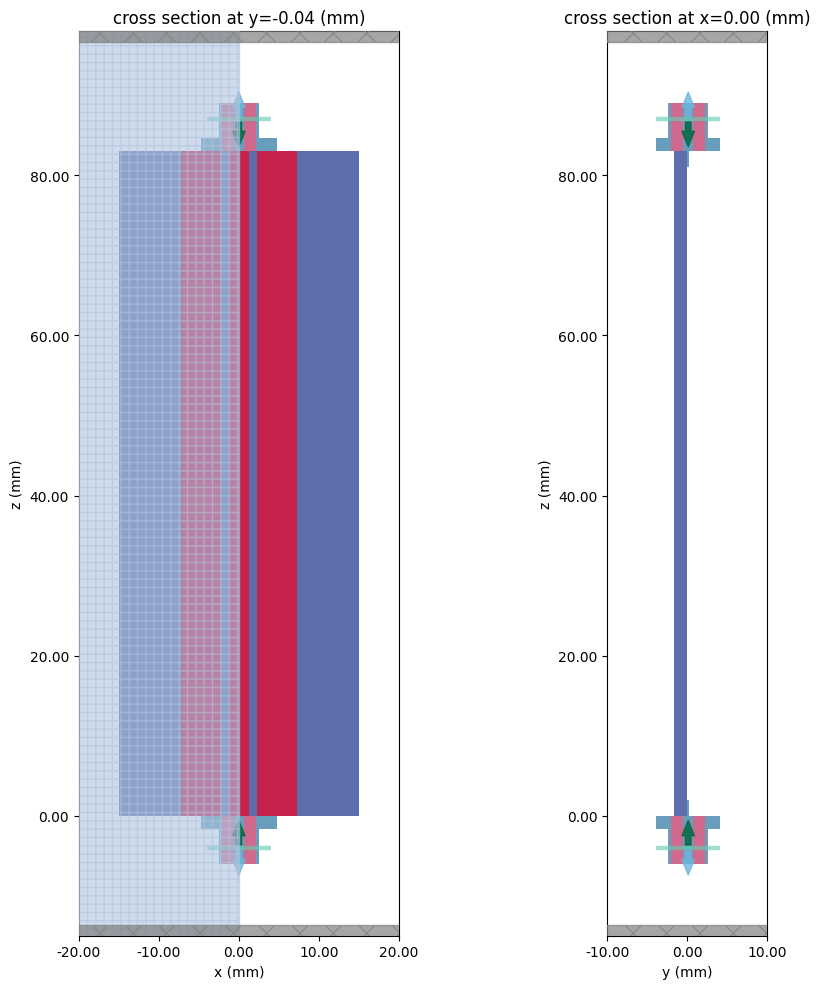
The grid in the SMA-CPW transition region is shown below. The mesh override regions are boxed with dotted black lines.
[17]:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10), tight_layout=True)
tcm.simulation.plot_grid(y=-T - H / 2, ax=ax)
tcm.plot_sim(
y=-T - H / 2, ax=ax, monitor_alpha=0, hlim=(-20 * mm, 20 * mm), vlim=(-10 * mm, 10 * mm)
)
plt.show()
We can also visualize the setup in 3D.
[18]:
sim.plot_3d()
Running the Simulation#
The simulation is executed below.
[19]:
tcm_data = web.run(tcm, task_name="sma_connector", path="data/sma_connector.hdf5")
14:18:27 EDT Created task 'sma_connector' with resource_id 'sid-7d07b37a-6775-426c-bdf3-0aa77befce63' and task_type 'RF'.
View task using web UI at 'https://tidy3d.simulation.cloud/rf?taskId=pa-4b736473-5db4-4765-a6 50-d31032d7773b'.
Task folder: 'default'.
14:18:31 EDT Child simulation subtasks are being uploaded to - WP2@0: 'rf-b83af70a-a477-43f4-9b93-d1c9fb469f97' - WP1@0: 'rf-3fa4cc77-df2a-4d9e-9afb-d852c9f84238'
14:18:33 EDT Validating component modeler and subtask simulations...
Maximum FlexCredit cost: 0.461. Minimum cost depends on task execution details. Use 'web.real_cost(task_id)' to get the billed FlexCredit cost after a simulation run.
Component modeler batch validation has been successful.
14:18:34 EDT Subtasks status - sma_connector Group ID: 'pa-4b736473-5db4-4765-a650-d31032d7773b'
14:22:30 EDT Modeler has finished running successfully.
14:22:31 EDT Billed FlexCredit cost: 0.342. Minimum cost depends on task execution details. Use 'web.real_cost(task_id)' to get the billed FlexCredit cost after a simulation run.
14:23:06 EDT loading component modeler data from data/sma_connector.hdf5
Results#
Field Profile#
The field monitor data is accessed from the .data attribute of the TerminalComponentModelerData result. The key is in the format <wave port name>@<mode number>, for example WP1@0. (In this case, there is only one mode.)
[20]:
# Extract simulation data
sim_data = tcm_data.data["WP1@0"]
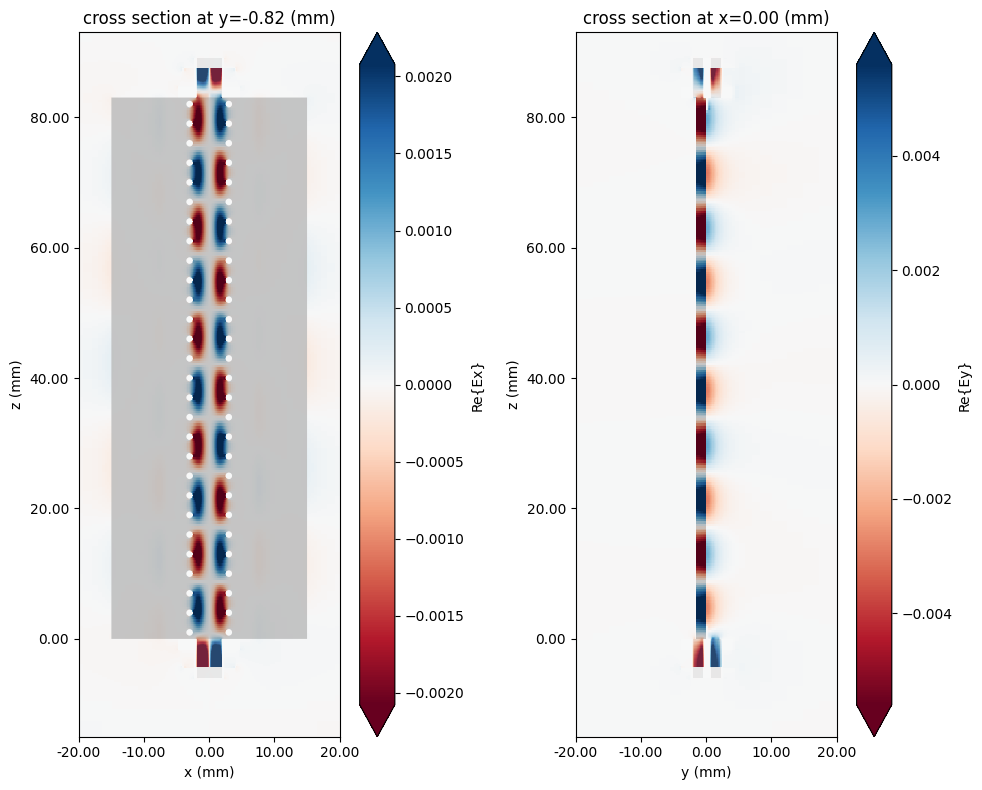
Below, the Ex and Ey field components are plotted along the top and side cross-sections respectively.
[21]:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 8), tight_layout=True)
f_plot = f_max
sim_data.plot_field("field in-plane", field_name="Ex", val="real", f=f_plot, ax=ax[0])
sim_data.plot_field("field cross section", "Ey", val="real", f=f_plot, ax=ax[1])
for axis in ax:
axis.set_ylim(-15 * mm, Lsub + 10 * mm)
axis.set_xlim(-20 * mm, 20 * mm)
plt.show()
S-parameters#
The S-matrix data is extracted using the smatrix() method. To access a specific S_ij parameter, use the corresponding port_in and port_out attributes. Note the use of np.conjugate to convert the S-parameter from the physics phase convention (current Tidy3D default) to the usual electrical engineering convention.
[22]:
# Extract S-matrix and S-parameters
smat = tcm_data.smatrix()
S11 = np.conjugate(smat.data.isel(port_in=0, port_out=0))
S21 = np.conjugate(smat.data.isel(port_in=0, port_out=1))
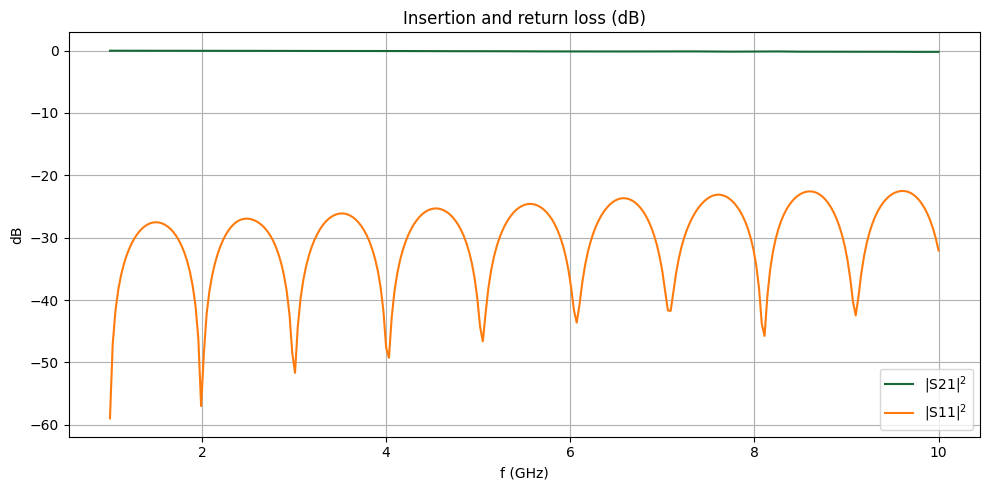
The insertion and return losses are plotted below. We observe excellent transmission and minimal reflection across the frequency band, indicating that the impedance of the SMA connector is well-matched to that of the on-board transmission line.
[23]:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5), tight_layout=True)
ax.plot(freqs / 1e9, 20 * np.log10(np.abs(S21)), label="|S21|$^2$")
ax.plot(freqs / 1e9, 20 * np.log10(np.abs(S11)), label="|S11|$^2$")
ax.set_title("Insertion and return loss (dB)")
ax.set_xlabel("f (GHz)")
ax.set_ylabel("dB")
ax.legend()
ax.grid()
plt.show()
[ ]: