Inverse design optimization of a compact grating coupler
Contents
Inverse design optimization of a compact grating coupler#
This notebook contains a long optimization. Running the entire notebook will cost about 20 FlexCredits and take several hours.
The ability to couple light in and out of photonic integrated circuits (PICs) is crucial for developing wafer-scale systems and tests. This need makes designing efficient and compact grating couplers an important task in the PIC development cycle. In this notebook, we will demonstrate how to use Tidy3D’s adjoint plugin to perform the inverse design of a compact 3D grating coupler. We will show how to improve design fabricability by enhancing permittivity binarization and controlling the device’s minimum feature size.
We start by importing our typical python packages, jax, tidy3d and its adjoint plugin.
[1]:
# Standard python imports.
from typing import List
import numpy as np
import scipy as sp
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
import os
import json
import pydantic as pd
from typing import Callable
# Import jax to be able to use automatic differentiation.
import jax.numpy as jnp
import jax.scipy as jsp
from jax import value_and_grad
# Import regular tidy3d.
import tidy3d as td
import tidy3d.web as web
# Import the components we need from the adjoint plugin.
from tidy3d.plugins.adjoint import (
JaxSimulation,
JaxBox,
JaxCustomMedium,
JaxStructure,
JaxSimulationData,
JaxDataArray,
JaxPermittivityDataset,
)
from tidy3d.plugins.adjoint.web import run
Grating Coupler Inverse Design Configuration#
The grating coupler inverse design begins with a rectangular design region connected to a \(Si\) waveguide. Throughout the optimization process, this initial structure evolves to convert a vertically incident Gaussian-like mode from an optical fiber into a guided mode and then funnel it into the \(Si\) waveguide.
We are considering a full-etched grating structure, so a \(SiO_{2}\) BOX layer is included. To reduce backreflection, we adjusted the fiber tilt angle to \(10^{\circ}\) [1, 2].
In the following block of code, you can find the parameters that can be modified to configure the grating coupler structure, optimization, and simulation setup. Special care should be devoted to the it_per_step and opt_steps variables bellow.
[2]:
# Geometric parameters.
w_thick = 0.22 # Waveguide thickness (um).
w_width = 0.5 # Waveguide width (um).
w_length = 1.0 # Waveguide length (um).
box_thick = 1.6 # SiO2 BOX thickness (um).
spot_size = 2.5 # Spot size of the input Gaussian field regarding a lensed fiber (um).
fiber_tilt = 10.0 # Fiber tilt angle (degrees).
src_offset = 0.05 # Distance between the source focus and device (um).
# Material.
nSi = 3.48 # Silicon refractive index.
nSiO2 = 1.44 # Silica refractive index.
# Design region parameters.
gc_width = 4.0 # Grating coupler width (um).
gc_length = 4.0 # Grating coupler length (um).
dr_grid_size = 0.02 # Grid size within the design region (um).
# Inverse design set up parameters.
#################################################################
# Total number of iterations = opt_steps x it_per_step.
it_per_step = 10 # Number of iterations per optimization step.
opt_steps = 15 # Number of optimization steps.
#################################################################
feature_size = 0.070 # Minimum feature size (um).
eta = 0.50 # Threshold value for the projection filter.
init_beta = 10 # Sharpness parameter for the projection filter.
del_beta = 10 # Increments of beta at each optimization step.
fom_name = "fom_field" # Name of the monitor used to compute the objective function.
# Inverse design data file.
output_file = "./misc/invdes_gc.json"
# Simulation wavelength.
wl = 1.55 # Central simulation wavelength (um).
bw = 0.06 # Simulation bandwidth (um).
n_wl = 61 # Number of wavelength points within the bandwidth.
Ckeching For a Previous Optimization#
If output_file is a valid file, the results of a previous optimization are loaded, then the optimization will continue from the last iteration step. If the optimization was completed, only the final structure will be simulated. The JSON file used in this notebook can be downloaded from our documentation repo.
[3]:
total_iter = opt_steps * it_per_step
iter_to_do = total_iter
prev_data = []
if os.path.isfile(output_file):
with open(output_file, "r", encoding="utf-8") as json_file:
prev_data = json.load(json_file)[0]
iter_to_do -= len(prev_data["obj_vals"])
print("Previous optimization data loaded from " + output_file)
print(f"Total iterations = {total_iter}")
print(f"Iterations to run = {iter_to_do}")
Total iterations = 150
Iterations to run = 150
Inverse Design Optimization Set Up#
We will calculate the values of some parameters used throughout the inverse design set up.
[4]:
# Minimum and maximum values for the permittivities.
eps_max = nSi**2
eps_min = 1.0
# Material definitions.
mat_si = td.Medium(permittivity=eps_max) # Waveguide material.
mat_sio2 = td.Medium(permittivity=nSiO2**2) # Substrate material.
# Wavelengths and frequencies.
wl_max = wl + bw / 2
wl_min = wl - bw / 2
wl_range = np.linspace(wl_min, wl_max, n_wl)
freq = td.C_0 / wl
freqs = td.C_0 / wl_range
freqw = 0.5 * (freqs[0] - freqs[-1])
run_time = 5e-12
# Computational domain size.
pml_spacing = 0.6 * wl
size_x = pml_spacing + w_length + gc_length
size_y = gc_width + 2 * pml_spacing
size_z = w_thick + box_thick + 2 * pml_spacing
center_z = size_z / 2 - pml_spacing - w_thick / 2
eff_inf = 1000
# Inverse design variables.
src_pos_z = w_thick / 2 + src_offset
mon_pos_x = -size_x / 2 + 0.25 * wl
mon_w = int(3 * w_width / dr_grid_size) * dr_grid_size
mon_h = int(5 * w_thick / dr_grid_size) * dr_grid_size
nx = int(gc_length / dr_grid_size)
ny = int(gc_width / dr_grid_size / 2.0)
npar = nx * ny
dr_size_x = nx * dr_grid_size
dr_size_y = 2 * ny * dr_grid_size
dr_center_x = -size_x / 2 + w_length + dr_size_x / 2
First, we will introduce the simulation components that do not change during optimization, such as the \(Si\) waveguide and \(SiO_{2}\) BOX layer. Additionally, we will include a Gaussian source to drive the simulations, and a mode monitor to compute the objective function.
[5]:
# Input/output waveguide.
waveguide = td.Structure(
geometry=td.Box.from_bounds(
rmin=(-eff_inf, -w_width / 2, -w_thick / 2),
rmax=(-size_x / 2 + w_length, w_width / 2, w_thick / 2),
),
medium=mat_si,
)
# SiO2 BOX layer.
sio2_substrate = td.Structure(
geometry=td.Box.from_bounds(
rmin=(-eff_inf, -eff_inf, -w_thick / 2 - box_thick),
rmax=(eff_inf, eff_inf, -w_thick / 2)
),
medium=mat_sio2,
)
# Si substrate.
si_substrate = td.Structure(
geometry=td.Box.from_bounds(
rmin=(-eff_inf, -eff_inf, -eff_inf),
rmax=(eff_inf, eff_inf, -w_thick / 2 - box_thick)
),
medium=mat_si,
)
# Gaussian source focused above the grating coupler.
gauss_source = td.GaussianBeam(
center=(dr_center_x, 0, src_pos_z),
size=(dr_size_x, dr_size_y, 0),
source_time=td.GaussianPulse(freq0=freq, fwidth=freqw),
pol_angle=np.pi / 2,
angle_theta=fiber_tilt * np.pi / 180.0,
direction="-",
num_freqs=7,
waist_radius=spot_size / 2,
)
# Monitor where we will compute the objective function from.
mode_spec = td.ModeSpec(num_modes=1, target_neff=nSi)
fom_monitor = td.ModeMonitor(
center=[mon_pos_x, 0, 0],
size=[0, mon_w, mon_h],
freqs=[freq],
mode_spec=mode_spec,
name=fom_name,
)
Now, we will define a random vector of initial design parameters or load a previously designed structure.
[6]:
init_par = np.random.uniform(0, 1, npar)
# Load parameters if continuing/visualizing a previous optimization:
if iter_to_do < total_iter:
init_par = np.array(prev_data["design_parameters"])
init_beta = prev_data["final_beta"]
# Only smooths the initial random distribution otherwise.
else:
init_par = sp.ndimage.gaussian_filter(init_par, 1)
Fabricability Improvements#
We will use jax to build functions that improve device fabricability. A classical conic density filter, which is popular in topology optimization problems, is used to enforce a minimum feature size specified by the feature_size variable. Next, a hyperbolic tangent projection function is applied to eliminate grayscale and obtain a binarized permittivity pattern. The beta parameter controls the sharpness of the transition in the projection function, and for better results, this
parameter should be gradually increased throughout the optimization process. Finally, the design parameters are transformed into permittivity values. For a detailed review of these methods, refer to [3].
[7]:
def get_eps(design_param, beta: float = 1.00, binarize: bool = False) -> np.ndarray:
"""Returns the permittivities after applying a conic density filter on design parameters
to enforce fabrication constraints, followed by a binarization projection function
which reduces grayscale.
Parameters:
design_param: np.ndarray
Vector of design parameters.
beta: float = 1.0
Sharpness parameter for the projection filter.
binarize: bool = False
Enforce binarization.
Returns:
eps: np.ndarray
Permittivity vector.
"""
# Reshapes the design parameters into a 2D matrix.
rho = np.reshape(design_param, (nx, ny))
# Builds the conic filter and apply it to design parameters.
filter_radius = np.ceil((feature_size * np.sqrt(3)) / dr_grid_size)
xy = np.linspace(-filter_radius, filter_radius, int(2 * filter_radius + 1))
xm, ym = np.meshgrid(xy, xy)
xy_rad = np.sqrt(xm**2 + ym**2)
kernel = jnp.where(filter_radius - xy_rad > 0, filter_radius - xy_rad, 0)
filt_den = jsp.signal.convolve(jnp.ones_like(rho), kernel, mode="same")
rho_dot = jsp.signal.convolve(rho, kernel, mode="same") / filt_den
# Applies a hyperbolic tangent binarization function.
rho_bar = (jnp.tanh(beta * eta) + jnp.tanh(beta * (rho_dot - eta))) / (
jnp.tanh(beta * eta) + jnp.tanh(beta * (1.0 - eta))
)
# Calculates the permittivities from the transformed design parameters.
eps = eps_min + (eps_max - eps_min) * rho_bar
if binarize:
eps = jnp.where(eps < (eps_min + eps_max) / 2, eps_min, eps_max)
else:
eps = jnp.where(eps < eps_min, eps_min, eps)
eps = jnp.where(eps > eps_max, eps_max, eps)
return eps
The permittivity values obtained from the design parameters are then used to build a JaxCustomMedium. As we will consider symmetry about the x-axis in the simulations, only the upper-half part of the design region needs to be populated. A JaxStructure built using the JaxCustomMedium will be returned by the following function:
[8]:
def update_design(eps, unfold: bool = False) -> List[JaxStructure]:
# Reflects the structure about the x-axis.
nyii = ny
y_min = 0
dr_s_y = dr_size_y / 2
dr_c_y = dr_s_y / 2
eps_val = jnp.array(eps).reshape((nx, ny, 1, 1))
if unfold:
nyii = 2 * ny
y_min = -dr_size_y / 2
dr_s_y = dr_size_y
dr_c_y = 0
eps_val = np.concatenate((np.fliplr(np.copy(eps_val)), eps_val), axis=1)
# Definition of the coordinates x,y along the design region.
coords_x = [(dr_center_x - dr_size_x / 2) + ix * dr_grid_size for ix in range(nx)]
coords_y = [y_min + iy * dr_grid_size for iy in range(nyii)]
coords = dict(x=coords_x, y=coords_y, z=[0], f=[freq])
# Creation of a custom medium using the values of the design parameters.
eps_components = {
f"eps_{dim}{dim}": JaxDataArray(values=eps_val, coords=coords) for dim in "xyz"
}
eps_dataset = JaxPermittivityDataset(**eps_components)
eps_medium = JaxCustomMedium(eps_dataset=eps_dataset)
box = JaxBox(center=(dr_center_x, dr_c_y, 0), size=(dr_size_x, dr_s_y, w_thick))
design_structure = JaxStructure(geometry=box, medium=eps_medium)
return [design_structure]
Next, we will write a function to return the JaxSimulation object. Note that we are using a MeshOverrideStructure to obtain a uniform mesh over the design region.
[9]:
def make_adjoint_sim(
design_param, beta: float = 1.00, unfold: bool = False, binarize: bool=False
) -> JaxSimulation:
# Builds the design region from the design parameters.
eps = get_eps(design_param, beta, binarize)
design_structure = update_design(eps, unfold=unfold)
# Creates a uniform mesh for the design region.
adjoint_dr_mesh = td.MeshOverrideStructure(
geometry=td.Box(
center=(dr_center_x, 0, 0), size=(dr_size_x, dr_size_y, w_thick)
),
dl=[dr_grid_size, dr_grid_size, dr_grid_size],
enforce=True,
)
return JaxSimulation(
size=[size_x, size_y, size_z],
center=[0, 0, -center_z],
grid_spec=td.GridSpec.auto(
wavelength=wl_max,
min_steps_per_wvl=15,
override_structures=[adjoint_dr_mesh],
),
symmetry=(0, -1, 0),
structures=[waveguide, sio2_substrate, si_substrate],
input_structures=design_structure,
sources=[gauss_source],
monitors=[],
output_monitors=[fom_monitor],
run_time=run_time,
subpixel=True,
)
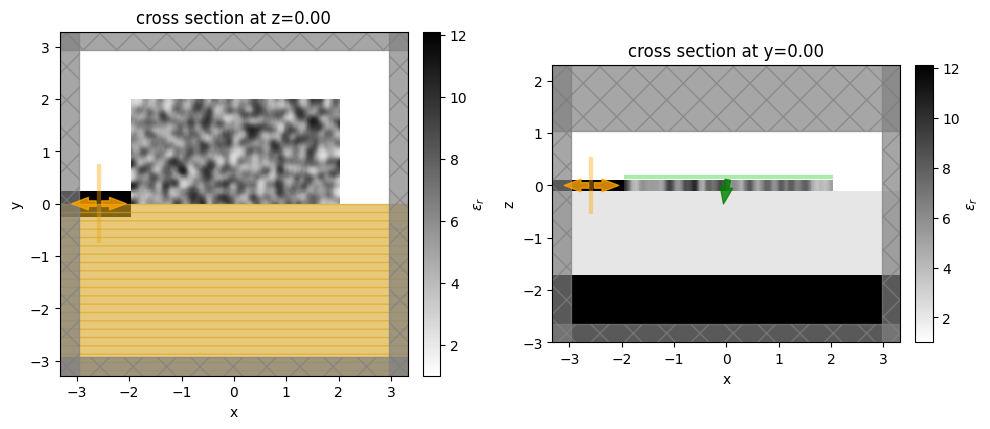
Let’s visualize the simulation set up and verify if all the elements are in their correct places.
[10]:
init_design = make_adjoint_sim(init_par, beta=init_beta)
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, tight_layout=True, figsize=(10, 10))
init_design.plot_eps(z=0, ax=ax1)
init_design.plot_eps(y=0, ax=ax2)
plt.show()
WARNING:jax._src.lib.xla_bridge:No GPU/TPU found, falling back to CPU. (Set TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL=0 and rerun for more info.)
Optimization#
We need to provide an objective function and its gradients with respect to the design parameters of the optimization algorithm.
Our figure-of-merit (FOM) is the coupling efficiency of the incident power into the fundamental transverse electric mode of the \(Si\) waveguide. The optimization algorithm will call the objective function at each iteration step. Therefore, the objective function will create the adjoint simulation, run it, and return the FOM value.
[11]:
# Figure of Merit (FOM) calculation.
def fom(sim_data: JaxSimulationData) -> float:
"""Return the power at the mode index of interest."""
output_amps = sim_data.output_data[0].amps
amp = output_amps.sel(direction="-", f=freq, mode_index=0)
return jnp.sum(jnp.abs(amp) ** 2)
# Objective function to be passed to the optimization algorithm.
def obj(
design_param, beta: float = 1.0, step_num: int = None, verbose: bool = False
) -> float:
sim = make_adjoint_sim(design_param, beta)
task_name = "inv_des"
if step_num:
task_name += f"_step_{step_num}"
sim_data = run(sim, task_name=task_name, verbose=verbose)
fom_val = fom(sim_data)
return fom_val
# Function to calculate the objective function value and its
# gradient with respect to the design parameters.
obj_grad = value_and_grad(obj)
Next, we will define an Optimizer class based on Adam gradient-descent algorithm to drive the inverse design process.
[12]:
class Optimizer(pd.BaseModel):
class Config:
arbitrary_types_allowed = True
val_and_grad: Callable = None # optimization function
parameters: np.ndarray # current state of the parameters
# General optimizer.
objective_history: list = []
param_history: list = []
num_it: int = 0 # current iteration number
class AdamOptimizer(Optimizer):
# Adam specific.
step_size: float = 0.02
beta1: float = 0.9
beta2: float = 0.999
epsilon: float = 1e-8
# Adam specific history parameters.
mt: np.ndarray = None
vt: np.ndarray = None
mt_history: list = []
vt_history: list = []
def __init__(self,
init_mt: np.ndarray=None,
init_vt: np.ndarray=None,
*args,
**kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
# Set mt and vt.
self.mt = np.zeros_like(self.parameters) if init_mt is None else init_mt
self.vt = np.zeros_like(self.parameters) if init_mt is None else init_vt
def step(self, *args, **kwargs):
"""args and kwargs are optional extra arguments passed to self.val_and_grad"""
val, grad = self.val_and_grad(self.parameters, *args, **kwargs)
grad = np.array(grad).reshape(self.parameters.shape)
# Display current status and update history variables.
print(f"At iteration {self.num_it}")
print(f"\tObjective function = {val:.4e}")
print(f"\tGrad_norm = {np.linalg.norm(grad):.4e}")
# Update Adam optimizer history.
self.num_it += 1
self.mt = self.beta1 * self.mt + (1 - self.beta1) * grad
self.vt = self.beta2 * self.vt + (1 - self.beta2) * grad ** 2
mt_hat = self.mt / (1 - self.beta1 ** self.num_it)
vt_hat = self.vt / (1 - self.beta2 ** self.num_it)
# Update parameters.
update = self.step_size * mt_hat / (np.sqrt(vt_hat) + self.epsilon)
self.parameters += update
# Update history.
self.objective_history.append(np.array(val))
self.param_history.append(self.parameters.copy())
self.mt_history.append(self.mt.copy())
self.vt_history.append(self.vt.copy())
Initialize a new optimizer or load the state from a previous optimization.
[13]:
if prev_data:
mt = np.array(prev_data["mt"])
vt = np.array(prev_data["vt"])
print("Restoring the previous optimizer state.")
else:
mt = np.zeros_like(init_par)
vt = np.zeros_like(init_par)
print("Initializing a new optimizer.")
optimizer = AdamOptimizer(
val_and_grad=obj_grad,
parameters=init_par,
init_mt=mt,
init_vt=vt
)
Initializing a new optimizer.
Now, we are ready to run the optimization!
[14]:
td.config.logging_level='ERROR'
# Run a new optimization or load the previous results.
final_beta = init_beta
if iter_to_do == 0:
final_par = init_par
obj_vals = prev_data["obj_vals"]
else:
for iteration in range(total_iter - iter_to_do, total_iter):
step = iteration // it_per_step
beta = step * del_beta + init_beta
final_beta = beta
print(f"Step {step}, beta = {beta}")
optimizer.step(beta=beta)
# Saves the optimization data into a json file.
data = [
{
"design_parameters": optimizer.param_history[-1].tolist(),
"final_beta": beta,
"obj_vals": np.array(optimizer.objective_history).tolist(),
"mt": optimizer.mt_history[-1].tolist(),
"vt": optimizer.vt_history[-1].tolist(),
}
]
json_string = json.dumps(data)
with open(output_file, "w", encoding="utf-8") as file_json:
file_json.write(json_string)
# Gets the final parameters and the objective values history.
final_par = optimizer.param_history[-1] # note: not optimizer.parameters as this has been stepped already
if prev_data:
obj_vals = np.array(prev_data["obj_vals"] + optimizer.objective_history).ravel()
else:
obj_vals = np.array(optimizer.objective_history).ravel()
Step 0, beta = 10
At iteration 0
Objective function = 7.8787e-05
Grad_norm = 7.3158e-04
Step 0, beta = 10
At iteration 1
Objective function = 4.8018e-02
Grad_norm = 3.1627e-02
Step 0, beta = 10
At iteration 2
Objective function = 1.6368e-01
Grad_norm = 5.7410e-02
Step 0, beta = 10
At iteration 3
Objective function = 3.0364e-01
Grad_norm = 1.5769e-01
Step 0, beta = 10
At iteration 4
Objective function = 3.6633e-01
Grad_norm = 1.1269e-01
Step 0, beta = 10
At iteration 5
Objective function = 4.6106e-01
Grad_norm = 4.4629e-02
Step 0, beta = 10
At iteration 6
Objective function = 4.8594e-01
Grad_norm = 5.9591e-02
Step 0, beta = 10
At iteration 7
Objective function = 5.1013e-01
Grad_norm = 3.9100e-02
Step 0, beta = 10
At iteration 8
Objective function = 5.3420e-01
Grad_norm = 1.9559e-02
Step 0, beta = 10
At iteration 9
Objective function = 5.5337e-01
Grad_norm = 1.3574e-02
Step 1, beta = 20
At iteration 10
Objective function = 3.9854e-01
Grad_norm = 5.3562e-02
Step 1, beta = 20
At iteration 11
Objective function = 5.2260e-01
Grad_norm = 3.4804e-02
Step 1, beta = 20
At iteration 12
Objective function = 5.4442e-01
Grad_norm = 4.8332e-02
Step 1, beta = 20
At iteration 13
Objective function = 5.2761e-01
Grad_norm = 4.3154e-02
Step 1, beta = 20
At iteration 14
Objective function = 5.4339e-01
Grad_norm = 3.4879e-02
Step 1, beta = 20
At iteration 15
Objective function = 5.8152e-01
Grad_norm = 2.4981e-02
Step 1, beta = 20
At iteration 16
Objective function = 5.8416e-01
Grad_norm = 2.3618e-02
Step 1, beta = 20
At iteration 17
Objective function = 5.8323e-01
Grad_norm = 2.2622e-02
Step 1, beta = 20
At iteration 18
Objective function = 5.8257e-01
Grad_norm = 2.7430e-02
Step 1, beta = 20
At iteration 19
Objective function = 5.9669e-01
Grad_norm = 1.8816e-02
Step 2, beta = 30
At iteration 20
Objective function = 5.8909e-01
Grad_norm = 2.2657e-02
Step 2, beta = 30
At iteration 21
Objective function = 5.9887e-01
Grad_norm = 3.5007e-02
Step 2, beta = 30
At iteration 22
Objective function = 5.9446e-01
Grad_norm = 3.7143e-02
Step 2, beta = 30
At iteration 23
Objective function = 6.0662e-01
Grad_norm = 2.2223e-02
Step 2, beta = 30
At iteration 24
Objective function = 6.1492e-01
Grad_norm = 3.7760e-02
Step 2, beta = 30
At iteration 25
Objective function = 6.2052e-01
Grad_norm = 3.1330e-02
Step 2, beta = 30
At iteration 26
Objective function = 6.2352e-01
Grad_norm = 2.3044e-02
Step 2, beta = 30
At iteration 27
Objective function = 6.2643e-01
Grad_norm = 3.7923e-02
Step 2, beta = 30
At iteration 28
Objective function = 6.3499e-01
Grad_norm = 2.7934e-02
Step 2, beta = 30
At iteration 29
Objective function = 6.4088e-01
Grad_norm = 2.1197e-02
Step 3, beta = 40
At iteration 30
Objective function = 6.2578e-01
Grad_norm = 6.6360e-02
Step 3, beta = 40
At iteration 31
Objective function = 6.2692e-01
Grad_norm = 6.8806e-02
Step 3, beta = 40
At iteration 32
Objective function = 6.4573e-01
Grad_norm = 1.6920e-02
Step 3, beta = 40
At iteration 33
Objective function = 6.4124e-01
Grad_norm = 5.7398e-02
Step 3, beta = 40
At iteration 34
Objective function = 6.4168e-01
Grad_norm = 6.9137e-02
Step 3, beta = 40
At iteration 35
Objective function = 6.5455e-01
Grad_norm = 1.8951e-02
Step 3, beta = 40
At iteration 36
Objective function = 6.4892e-01
Grad_norm = 6.0518e-02
Step 3, beta = 40
At iteration 37
Objective function = 6.5222e-01
Grad_norm = 5.5811e-02
Step 3, beta = 40
At iteration 38
Objective function = 6.6217e-01
Grad_norm = 1.3080e-02
Step 3, beta = 40
At iteration 39
Objective function = 6.5283e-01
Grad_norm = 6.4406e-02
Step 4, beta = 50
At iteration 40
Objective function = 6.6467e-01
Grad_norm = 1.4755e-02
Step 4, beta = 50
At iteration 41
Objective function = 6.5750e-01
Grad_norm = 6.4817e-02
Step 4, beta = 50
At iteration 42
Objective function = 6.5981e-01
Grad_norm = 6.3940e-02
Step 4, beta = 50
At iteration 43
Objective function = 6.6727e-01
Grad_norm = 3.3743e-02
Step 4, beta = 50
At iteration 44
Objective function = 6.6944e-01
Grad_norm = 4.2831e-02
Step 4, beta = 50
At iteration 45
Objective function = 6.7020e-01
Grad_norm = 3.2677e-02
Step 4, beta = 50
At iteration 46
Objective function = 6.7406e-01
Grad_norm = 2.7373e-02
Step 4, beta = 50
At iteration 47
Objective function = 6.7144e-01
Grad_norm = 3.0082e-02
Step 4, beta = 50
At iteration 48
Objective function = 6.7817e-01
Grad_norm = 1.1559e-02
Step 4, beta = 50
At iteration 49
Objective function = 6.7394e-01
Grad_norm = 3.7587e-02
Step 5, beta = 60
At iteration 50
Objective function = 6.7873e-01
Grad_norm = 1.6116e-02
Step 5, beta = 60
At iteration 51
Objective function = 6.7827e-01
Grad_norm = 2.8026e-02
Step 5, beta = 60
At iteration 52
Objective function = 6.7681e-01
Grad_norm = 3.5310e-02
Step 5, beta = 60
At iteration 53
Objective function = 6.8095e-01
Grad_norm = 1.6904e-02
Step 5, beta = 60
At iteration 54
Objective function = 6.8135e-01
Grad_norm = 2.1578e-02
Step 5, beta = 60
At iteration 55
Objective function = 6.8237e-01
Grad_norm = 2.9715e-02
Step 5, beta = 60
At iteration 56
Objective function = 6.8458e-01
Grad_norm = 1.3201e-02
Step 5, beta = 60
At iteration 57
Objective function = 6.8457e-01
Grad_norm = 2.6202e-02
Step 5, beta = 60
At iteration 58
Objective function = 6.8622e-01
Grad_norm = 2.1887e-02
Step 5, beta = 60
At iteration 59
Objective function = 6.8759e-01
Grad_norm = 1.4890e-02
Step 6, beta = 70
At iteration 60
Objective function = 6.8776e-01
Grad_norm = 1.8331e-02
Step 6, beta = 70
At iteration 61
Objective function = 6.8853e-01
Grad_norm = 1.1289e-02
Step 6, beta = 70
At iteration 62
Objective function = 6.8889e-01
Grad_norm = 1.7278e-02
Step 6, beta = 70
At iteration 63
Objective function = 6.8997e-01
Grad_norm = 1.4952e-02
Step 6, beta = 70
At iteration 64
Objective function = 6.9056e-01
Grad_norm = 1.3550e-02
Step 6, beta = 70
At iteration 65
Objective function = 6.9190e-01
Grad_norm = 1.0412e-02
Step 6, beta = 70
At iteration 66
Objective function = 6.9186e-01
Grad_norm = 1.3028e-02
Step 6, beta = 70
At iteration 67
Objective function = 6.9353e-01
Grad_norm = 5.8804e-03
Step 6, beta = 70
At iteration 68
Objective function = 6.9393e-01
Grad_norm = 9.3477e-03
Step 6, beta = 70
At iteration 69
Objective function = 6.9438e-01
Grad_norm = 1.2194e-02
Step 7, beta = 80
At iteration 70
Objective function = 6.9466e-01
Grad_norm = 1.8469e-02
Step 7, beta = 80
At iteration 71
Objective function = 6.9380e-01
Grad_norm = 2.6154e-02
Step 7, beta = 80
At iteration 72
Objective function = 6.9387e-01
Grad_norm = 2.3957e-02
Step 7, beta = 80
At iteration 73
Objective function = 6.9242e-01
Grad_norm = 3.4005e-02
Step 7, beta = 80
At iteration 74
Objective function = 6.9083e-01
Grad_norm = 4.0479e-02
Step 7, beta = 80
At iteration 75
Objective function = 6.9177e-01
Grad_norm = 4.6328e-02
Step 7, beta = 80
At iteration 76
Objective function = 6.8915e-01
Grad_norm = 5.8739e-02
Step 7, beta = 80
At iteration 77
Objective function = 6.9357e-01
Grad_norm = 4.5696e-02
Step 7, beta = 80
At iteration 78
Objective function = 6.9759e-01
Grad_norm = 2.0101e-02
Step 7, beta = 80
At iteration 79
Objective function = 6.9816e-01
Grad_norm = 3.0047e-02
Step 8, beta = 90
At iteration 80
Objective function = 6.9263e-01
Grad_norm = 4.5487e-02
Step 8, beta = 90
At iteration 81
Objective function = 6.9537e-01
Grad_norm = 4.0683e-02
Step 8, beta = 90
At iteration 82
Objective function = 6.9924e-01
Grad_norm = 2.7934e-02
Step 8, beta = 90
At iteration 83
Objective function = 6.9956e-01
Grad_norm = 2.1489e-02
Step 8, beta = 90
At iteration 84
Objective function = 6.9826e-01
Grad_norm = 4.0911e-02
Step 8, beta = 90
At iteration 85
Objective function = 6.9955e-01
Grad_norm = 3.1945e-02
Step 8, beta = 90
At iteration 86
Objective function = 7.0155e-01
Grad_norm = 2.1972e-02
Step 8, beta = 90
At iteration 87
Objective function = 6.9874e-01
Grad_norm = 3.8842e-02
Step 8, beta = 90
At iteration 88
Objective function = 7.0086e-01
Grad_norm = 3.0929e-02
Step 8, beta = 90
At iteration 89
Objective function = 7.0276e-01
Grad_norm = 1.7881e-02
Step 9, beta = 100
At iteration 90
Objective function = 7.0241e-01
Grad_norm = 3.2847e-02
Step 9, beta = 100
At iteration 91
Objective function = 6.9862e-01
Grad_norm = 4.5569e-02
Step 9, beta = 100
At iteration 92
Objective function = 7.0254e-01
Grad_norm = 3.0195e-02
Step 9, beta = 100
At iteration 93
Objective function = 7.0349e-01
Grad_norm = 2.5936e-02
Step 9, beta = 100
At iteration 94
Objective function = 6.9935e-01
Grad_norm = 4.3035e-02
Step 9, beta = 100
At iteration 95
Objective function = 7.0155e-01
Grad_norm = 3.6590e-02
Step 9, beta = 100
At iteration 96
Objective function = 7.0097e-01
Grad_norm = 4.0512e-02
Step 9, beta = 100
At iteration 97
Objective function = 6.9925e-01
Grad_norm = 5.6556e-02
Step 9, beta = 100
At iteration 98
Objective function = 7.0168e-01
Grad_norm = 4.2130e-02
Step 9, beta = 100
At iteration 99
Objective function = 7.0247e-01
Grad_norm = 3.6289e-02
Step 10, beta = 110
At iteration 100
Objective function = 7.0552e-01
Grad_norm = 2.3682e-02
Step 10, beta = 110
At iteration 101
Objective function = 7.0666e-01
Grad_norm = 1.4257e-02
Step 10, beta = 110
At iteration 102
Objective function = 7.0521e-01
Grad_norm = 3.0919e-02
Step 10, beta = 110
At iteration 103
Objective function = 7.0437e-01
Grad_norm = 3.4261e-02
Step 10, beta = 110
At iteration 104
Objective function = 7.0451e-01
Grad_norm = 3.7208e-02
Step 10, beta = 110
At iteration 105
Objective function = 7.0310e-01
Grad_norm = 4.5987e-02
Step 10, beta = 110
At iteration 106
Objective function = 7.0444e-01
Grad_norm = 4.5127e-02
Step 10, beta = 110
At iteration 107
Objective function = 7.0541e-01
Grad_norm = 3.7913e-02
Step 10, beta = 110
At iteration 108
Objective function = 7.0637e-01
Grad_norm = 3.1812e-02
Step 10, beta = 110
At iteration 109
Objective function = 7.0838e-01
Grad_norm = 2.4365e-02
Step 11, beta = 120
At iteration 110
Objective function = 7.0941e-01
Grad_norm = 1.5828e-02
Step 11, beta = 120
At iteration 111
Objective function = 7.0999e-01
Grad_norm = 1.1399e-02
Step 11, beta = 120
At iteration 112
Objective function = 7.1044e-01
Grad_norm = 1.3538e-02
Step 11, beta = 120
At iteration 113
Objective function = 7.1036e-01
Grad_norm = 1.1503e-02
Step 11, beta = 120
At iteration 114
Objective function = 7.1106e-01
Grad_norm = 1.3215e-02
Step 11, beta = 120
At iteration 115
Objective function = 7.0978e-01
Grad_norm = 2.4962e-02
Step 11, beta = 120
At iteration 116
Objective function = 7.0811e-01
Grad_norm = 3.9985e-02
Step 11, beta = 120
At iteration 117
Objective function = 7.0220e-01
Grad_norm = 6.0520e-02
Step 11, beta = 120
At iteration 118
Objective function = 6.9057e-01
Grad_norm = 8.7708e-02
Step 11, beta = 120
At iteration 119
Objective function = 6.8557e-01
Grad_norm = 9.6025e-02
Step 12, beta = 130
At iteration 120
Objective function = 7.0355e-01
Grad_norm = 5.1987e-02
Step 12, beta = 130
At iteration 121
Objective function = 7.0868e-01
Grad_norm = 3.1631e-02
Step 12, beta = 130
At iteration 122
Objective function = 6.9763e-01
Grad_norm = 6.5204e-02
Step 12, beta = 130
At iteration 123
Objective function = 7.1038e-01
Grad_norm = 2.0649e-02
Step 12, beta = 130
At iteration 124
Objective function = 7.0522e-01
Grad_norm = 4.4686e-02
Step 12, beta = 130
At iteration 125
Objective function = 7.0632e-01
Grad_norm = 3.8831e-02
Step 12, beta = 130
At iteration 126
Objective function = 7.1051e-01
Grad_norm = 2.4704e-02
Step 12, beta = 130
At iteration 127
Objective function = 7.0595e-01
Grad_norm = 4.6373e-02
Step 12, beta = 130
At iteration 128
Objective function = 7.1229e-01
Grad_norm = 6.4697e-03
Step 12, beta = 130
At iteration 129
Objective function = 7.0779e-01
Grad_norm = 3.5093e-02
Step 13, beta = 140
At iteration 130
Objective function = 7.1229e-01
Grad_norm = 8.1188e-03
Step 13, beta = 140
At iteration 131
Objective function = 7.0907e-01
Grad_norm = 3.3656e-02
Step 13, beta = 140
At iteration 132
Objective function = 7.1239e-01
Grad_norm = 1.7798e-02
Step 13, beta = 140
At iteration 133
Objective function = 7.1129e-01
Grad_norm = 2.4917e-02
Step 13, beta = 140
At iteration 134
Objective function = 7.1160e-01
Grad_norm = 2.4725e-02
Step 13, beta = 140
At iteration 135
Objective function = 7.1328e-01
Grad_norm = 1.3879e-02
Step 13, beta = 140
At iteration 136
Objective function = 7.1158e-01
Grad_norm = 2.6793e-02
Step 13, beta = 140
At iteration 137
Objective function = 7.1391e-01
Grad_norm = 5.4024e-03
Step 13, beta = 140
At iteration 138
Objective function = 7.1211e-01
Grad_norm = 2.5809e-02
Step 13, beta = 140
At iteration 139
Objective function = 7.1435e-01
Grad_norm = 7.9815e-03
Step 14, beta = 150
At iteration 140
Objective function = 7.1318e-01
Grad_norm = 2.0542e-02
Step 14, beta = 150
At iteration 141
Objective function = 7.1413e-01
Grad_norm = 1.5115e-02
Step 14, beta = 150
At iteration 142
Objective function = 7.1408e-01
Grad_norm = 1.4412e-02
Step 14, beta = 150
At iteration 143
Objective function = 7.1402e-01
Grad_norm = 1.8037e-02
Step 14, beta = 150
At iteration 144
Objective function = 7.1497e-01
Grad_norm = 1.0758e-02
Step 14, beta = 150
At iteration 145
Objective function = 7.1437e-01
Grad_norm = 1.5867e-02
Step 14, beta = 150
At iteration 146
Objective function = 7.1539e-01
Grad_norm = 3.4644e-03
Step 14, beta = 150
At iteration 147
Objective function = 7.1483e-01
Grad_norm = 1.5382e-02
Step 14, beta = 150
At iteration 148
Objective function = 7.1564e-01
Grad_norm = 8.0472e-03
Step 14, beta = 150
At iteration 149
Objective function = 7.1526e-01
Grad_norm = 1.3292e-02
Optimization Results#
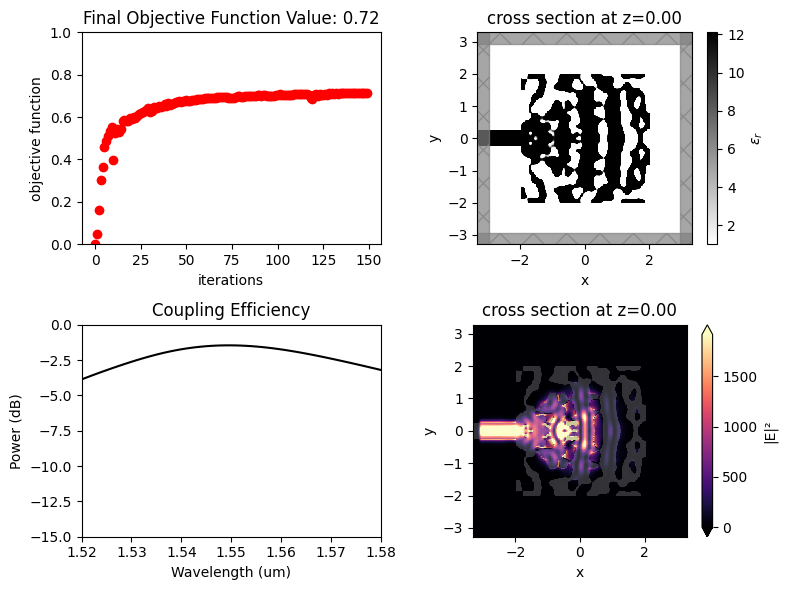
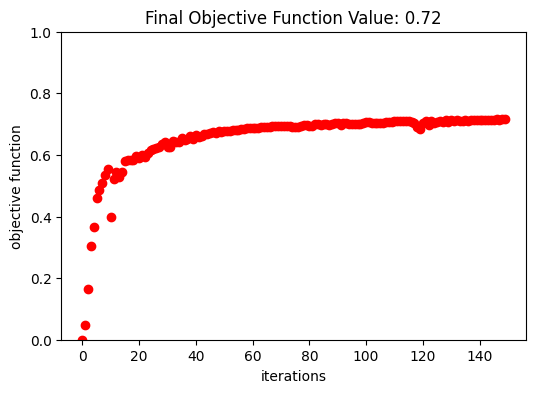
After 150 iterations, a coupling efficiency value of 0.71 (-1.48 dB) was achieved at the central wavelength.
[15]:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(6, 4))
ax.plot(obj_vals, "ro")
ax.set_xlabel("iterations")
ax.set_ylabel("objective function")
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax.set_title(f"Final Objective Function Value: {obj_vals[-1]:.2f}")
plt.show()
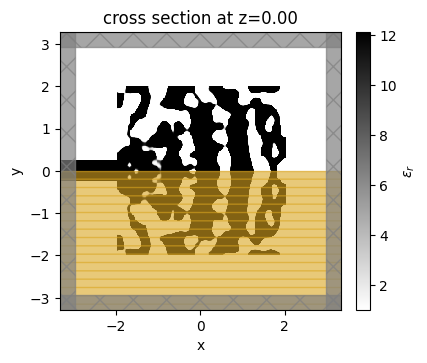
The final grating coupler structure is well binarized, with mostly black (eps_max) and white (eps_min) regions.
[20]:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(4, 4))
sim_final = make_adjoint_sim(final_par, beta=final_beta, unfold=True)
sim_final = sim_final.to_simulation()[0]
sim_final.plot_eps(z=0, source_alpha=0, monitor_alpha=0, ax=ax)
plt.show()
Once the inverse design is complete, we can visualize the field distributions and the wavelength dependent coupling efficiency.
[17]:
# Field monitors to visualize the final fields.
field_xy = td.FieldMonitor(
size=(td.inf, td.inf, 0),
freqs=[freq],
name="field_xy",
)
field_xz = td.FieldMonitor(
size=(td.inf, 0, td.inf),
freqs=[freq],
name="field_xz",
)
# Monitor to compute the grating coupler efficiency.
gc_efficiency = td.ModeMonitor(
center=[mon_pos_x, 0, 0],
size=[0, mon_w, mon_h],
freqs=freqs,
mode_spec=mode_spec,
name="gc_efficiency",
)
sim_final = sim_final.copy(update=dict(monitors=(field_xy, field_xz, gc_efficiency)))
sim_data_final = web.run(sim_final, task_name="inv_des_final")
View task using web UI at webapi.py:189 'https://tidy3d.simulation.cloud/workbench?taskId=fdve-4d076c97-fb0c-49c2-933e-ef54b373526 5v1'.
[18]:
mode_amps = sim_data_final["gc_efficiency"]
coeffs_f = mode_amps.amps.sel(direction="-")
power_0 = np.abs(coeffs_f.sel(mode_index=0)) ** 2
power_0_db = 10 * np.log10(power_0)
sim_plot = sim_final.updated_copy(symmetry=(0, 0, 0), monitors=(field_xy, field_xz, gc_efficiency))
sim_data_plot = sim_data_final.updated_copy(simulation=sim_plot)
f, ax = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(8, 6), tight_layout=True)
sim_plot.plot_eps(z=0, source_alpha=0, monitor_alpha=0, ax=ax[0, 1])
ax[1, 0].plot(wl_range, power_0_db, "-k")
ax[1, 0].set_xlabel("Wavelength (um)")
ax[1, 0].set_ylabel("Power (dB)")
ax[1, 0].set_ylim(-15, 0)
ax[1, 0].set_xlim(wl - bw / 2, wl + bw / 2)
ax[1, 0].set_title("Coupling Efficiency")
sim_data_plot.plot_field("field_xy", "E", "abs^2", z=0, ax=ax[1, 1])
ax[0, 0].plot(obj_vals, "ro")
ax[0, 0].set_xlabel("iterations")
ax[0, 0].set_ylabel("objective function")
ax[0, 0].set_ylim(0, 1)
ax[0, 0].set_title(f"Final Objective Function Value: {obj_vals[-1]:.2f}")
plt.show()